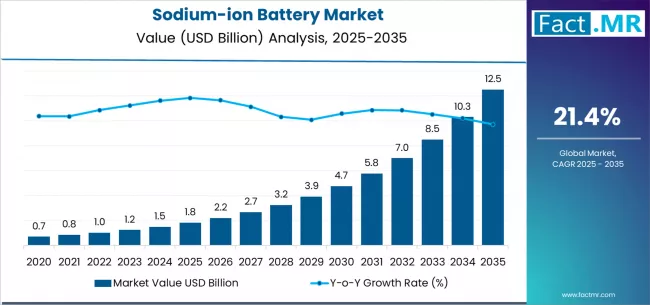
As the global demand for renewable energy and electric mobility grows, energy storage technologies are undergoing rapid transformation. Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as a promising alternative to lithium-ion systems, offering cost-effectiveness, material abundance, and environmentally friendly characteristics.
Sodium-ion batteries are designed to store and deliver electrical energy efficiently, making them suitable for applications ranging from grid storage to electric vehicles and portable electronics. Their reliance on sodium—an abundant and widely available material—positions them as a sustainable solution to address the resource constraints and rising costs associated with lithium-ion technologies.
Market Overview
The sodium-ion battery market encompasses a range of technologies designed for high performance, safety, and durability. These batteries operate on the same electrochemical principles as lithium-ion systems but substitute lithium with sodium ions, providing similar energy storage capabilities at a potentially lower cost.
SIBs offer several advantages, including thermal stability, safer chemistry, and the ability to function efficiently under varying temperatures. Additionally, advancements in cathode and anode materials, electrolyte formulations, and cell designs are enhancing energy density, charge-discharge rates, and cycle life, making sodium-ion batteries increasingly viable for commercial adoption.
Sustainability is a core driver, as sodium-ion batteries reduce dependency on critical minerals like lithium and cobalt. This aligns with global efforts to create environmentally responsible energy storage solutions while maintaining the performance required for modern applications.
Regional Insights
The adoption of sodium-ion batteries is expanding globally, influenced by regional energy policies, industrial growth, and renewable integration:
- North America is focusing on innovation and pilot projects, leveraging research institutions and startups to advance SIB technology. Applications in grid storage and industrial energy systems are gaining traction.
- Europe is accelerating SIB adoption due to stringent environmental regulations, incentives for clean energy storage, and investments in sustainable battery manufacturing. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are actively exploring sodium-ion solutions for both stationary and mobility applications.
- Asia Pacific is emerging as a key growth region, driven by demand from electric vehicle manufacturers, renewable energy projects, and government-backed battery production initiatives in China, India, and Japan.
- Middle East & Africa show potential in large-scale renewable integration, particularly for grid balancing and off-grid energy storage, where cost-effectiveness and material availability are critical considerations.
Regional diversity in adoption highlights sodium-ion batteries’ versatility, serving applications from industrial energy storage to consumer electronics in different markets.
Key Trends & Forecast
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of the sodium-ion battery market:
- Cost-Effective Energy Storage: Sodium’s abundance and lower material costs make SIBs an attractive alternative to lithium-ion batteries, especially for large-scale storage projects.
- Grid Integration: SIBs are increasingly deployed in renewable energy systems for peak shaving, load leveling, and stabilizing intermittent energy sources such as solar and wind.
- Electric Mobility Adoption: While lithium-ion remains dominant, sodium-ion batteries are being explored for low-to-mid-range electric vehicles due to safety, temperature tolerance, and lower cost potential.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in cathode and anode chemistries, solid-state electrolytes, and cell architecture are improving performance, energy density, and lifespan, narrowing the gap with lithium-ion systems.
- Sustainability and Recycling: Sodium-ion batteries offer environmentally friendly end-of-life options and reduced reliance on scarce minerals, aligning with global circular economy initiatives.
These trends indicate a market moving toward scalable, affordable, and sustainable energy storage solutions capable of complementing existing technologies.
Applications & End-Use Outlook
Sodium-ion batteries are being adopted across diverse sectors, reflecting their versatility and efficiency:
- Grid and Stationary Storage: SIBs provide cost-effective energy storage for renewable energy integration, backup power, and microgrid applications. They help stabilize voltage fluctuations and optimize energy distribution in both urban and remote areas.
- Electric Vehicles: Sodium-ion batteries are being tested for use in electric two-wheelers, buses, and low-range passenger vehicles, offering a safer and potentially more affordable alternative to lithium-ion systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Portable electronics, power banks, and household energy storage units can leverage SIBs for reliable, durable, and cost-efficient performance.
- Industrial Applications: SIBs are deployed in material handling, emergency power systems, and manufacturing operations requiring stable and efficient energy storage solutions.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Utility-scale solar and wind projects utilize sodium-ion batteries for grid balancing, frequency regulation, and energy arbitrage, ensuring consistent power supply in fluctuating conditions.
The wide range of applications highlights the growing relevance of sodium-ion batteries as a versatile and scalable energy storage technology.
Competitive Landscape
The sodium-ion battery market features a mix of established battery manufacturers, innovative startups, and research institutions working to commercialize the technology. Companies are investing in material innovation, cell design, and large-scale production capacity to make SIBs commercially viable.
Collaborations between battery developers, automotive OEMs, and renewable energy companies are accelerating adoption. Additionally, partnerships with universities and research centers are fueling technological breakthroughs in energy density, cycle life, and cost reduction.
Aftermarket services such as maintenance, recycling, and energy management solutions are emerging as key differentiators for companies seeking to enhance the value proposition of sodium-ion batteries.
Conclusion
The sodium-ion battery market represents a critical evolution in energy storage, offering a sustainable, cost-effective, and safe alternative to conventional lithium-ion systems. With applications spanning grid storage, electric mobility, consumer electronics, and industrial operations, SIBs are poised to address the growing global demand for reliable, environmentally friendly energy solutions.
Advances in material science, cell design, and manufacturing are closing the performance gap with lithium-ion batteries, paving the way for broader commercial adoption. As energy systems worldwide strive for sustainability, safety, and efficiency, sodium-ion batteries are emerging as a key technology for powering the next generation of clean energy infrastructure.
In an era defined by renewable energy expansion and electrification, sodium-ion batteries offer the potential to balance cost, performance, and sustainability—shaping the future of energy storage across industries and geographies.
Browse Full Report – https://www.factmr.com/report/sodium-ion-battery-market