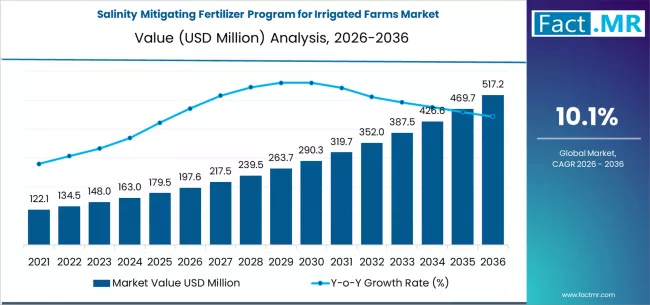
Soil salinity has emerged as a major challenge for irrigated agriculture, affecting crop yields, soil structure, and long-term farm productivity. As irrigation practices expand to meet global food demand, the accumulation of salts in agricultural soils has become increasingly difficult to manage. In response, salinity mitigating fertilizer programs are gaining recognition as an effective and sustainable approach to maintaining soil health and crop performance.
The salinity mitigating fertilizer program for irrigated farms market is evolving as farmers, agronomists, and agricultural input providers focus on integrated nutrient solutions that address salinity stress while supporting balanced crop nutrition. These programs are designed to improve soil conditions, enhance nutrient uptake, and promote resilient farming systems.
Market Overview
Salinity mitigating fertilizer programs combine specialized fertilizers, soil conditioners, and nutrient management strategies aimed at reducing the negative effects of salinity in irrigated soils. Rather than focusing solely on nutrient supply, these programs address underlying soil chemistry issues that restrict plant growth under saline conditions.
The market is driven by the increasing adoption of precision agriculture and soil health management practices. Farmers are moving toward customized fertilizer programs that consider water quality, soil type, crop requirements, and environmental conditions. This shift has encouraged the development of comprehensive salinity management solutions rather than standalone products.
Manufacturers and service providers are offering integrated programs that include product selection, application guidance, and agronomic support to maximize effectiveness.
Understanding Salinity Challenges in Irrigated Farms
Salinity in irrigated farms often results from the repeated use of mineral-rich irrigation water and inadequate drainage. Over time, soluble salts accumulate in the root zone, limiting water uptake by plants and disrupting nutrient balance. This can lead to reduced crop vigor, lower yields, and long-term soil degradation.
Salinity mitigating fertilizer programs aim to counter these effects by improving soil structure, enhancing calcium availability, and supporting beneficial microbial activity. These approaches help displace excess sodium, improve soil permeability, and create a more favorable root environment for crops.
By addressing salinity at both the soil and plant levels, these programs offer a proactive solution to a growing agricultural challenge.
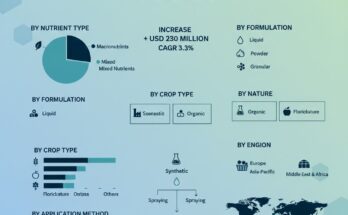
Product Types and Program Components
Salinity mitigating fertilizer programs typically include a combination of calcium-based fertilizers, sulfate-containing nutrients, organic amendments, and specialty soil conditioners. These components work together to improve soil aggregation, reduce sodium dominance, and enhance nutrient availability.
Some programs incorporate micronutrients and biostimulants to support plant stress tolerance and root development under saline conditions. Controlled-release and water-soluble fertilizers are also used to ensure efficient nutrient delivery in irrigated systems.
The growing emphasis on integrated nutrient management has led to the development of tailored programs that are adapted to specific crops, soil profiles, and irrigation practices.
Applications Across Crops and Farming Systems
These fertilizer programs are widely used across a range of irrigated crops, including cereals, fruits, vegetables, oilseeds, and forage crops. High-value crops grown under intensive irrigation often benefit significantly from salinity mitigation strategies due to their sensitivity to soil conditions.
In large-scale irrigated farming systems, salinity mitigating programs support consistent productivity and reduce the need for costly soil remediation measures. Small and medium-sized farms are also adopting these programs as part of broader efforts to improve soil health and input efficiency.
By integrating salinity management into regular fertilization practices, farmers can achieve long-term benefits without disrupting existing farm operations.
End-User Adoption Trends
Farmers and agricultural producers represent the primary end users of salinity mitigating fertilizer programs. Increasing awareness of soil health and sustainable farming practices has encouraged adoption across diverse agricultural regions.
Agricultural cooperatives and agribusinesses play a key role in promoting these programs by offering bundled solutions and technical support. Extension services and agronomists also contribute by educating farmers on the benefits of proactive salinity management.
As irrigation-dependent agriculture continues to expand, demand for effective salinity mitigation solutions is expected to grow steadily.
Regional Market Insights
Regions with extensive irrigated agriculture and arid or semi-arid climates are key markets for salinity mitigating fertilizer programs. In these areas, water quality and evaporation rates increase the risk of salt accumulation in soils.
Emerging agricultural regions are also experiencing growing demand as irrigation infrastructure develops and awareness of soil salinity issues increases. Government initiatives focused on sustainable water and soil management further support market expansion.
Global suppliers are tailoring their offerings to regional soil conditions and cropping systems, strengthening adoption across diverse geographies.
Key Trends and Innovations
One of the most important trends in the market is the integration of salinity mitigation with precision agriculture technologies. Soil testing, remote sensing, and data-driven decision tools are enabling more targeted fertilizer application and improved program effectiveness.
Sustainable and environmentally responsible formulations are also gaining traction, aligning with broader goals of reducing soil degradation and preserving natural resources. These innovations support long-term farm productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Additionally, collaboration between fertilizer manufacturers, research institutions, and farmers is driving continuous improvement in program design and performance.
Challenges and Market Constraints
Despite their benefits, salinity mitigating fertilizer programs face challenges related to awareness, cost considerations, and variability in field conditions. Effective implementation requires proper diagnosis of soil salinity levels and consistent management practices.
Limited access to technical expertise in some regions can also hinder adoption. Addressing these challenges through education, extension services, and affordable program options will be essential for broader market penetration.
Future Outlook
The future of the salinity mitigating fertilizer program for irrigated farms market is closely linked to global efforts to improve agricultural sustainability and food security. As climate variability and water scarcity intensify salinity risks, the importance of integrated soil and nutrient management solutions will continue to rise.
Advancements in fertilizer formulations, soil conditioners, and digital agriculture tools are expected to enhance program effectiveness and accessibility. With increasing focus on soil resilience, salinity mitigating fertilizer programs are set to become a core component of modern irrigated farming systems.
Conclusion
Salinity mitigating fertilizer programs play a vital role in addressing one of the most persistent challenges facing irrigated agriculture. By improving soil conditions and supporting balanced crop nutrition, these programs help farmers maintain productivity and protect long-term soil health.
As awareness grows and agricultural practices evolve, the adoption of comprehensive salinity mitigation strategies will continue to expand. For stakeholders seeking sustainable solutions in irrigated farming, understanding market trends and innovations offers valuable guidance for informed decision-making.
Browse Full Report – https://www.factmr.com/report/salinity-mitigating-fertilizer-program-for-irrigated-farms-market