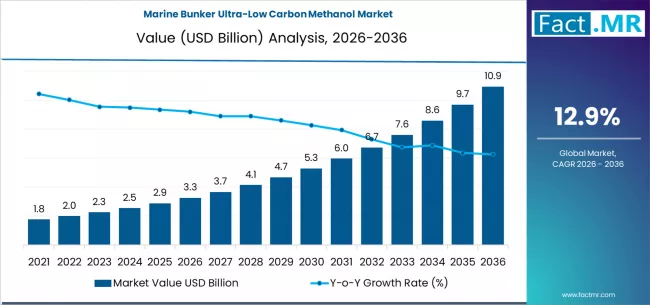
The maritime industry is undergoing a transformative shift toward sustainability, driven by stringent regulations on greenhouse gas emissions and the global push for cleaner fuels. Marine bunker ultra-low carbon methanol is emerging as a viable alternative to conventional heavy fuel oil, enabling ships to reduce carbon intensity without significant infrastructure overhauls. As shipping companies face growing pressure from regulators and cargo owners, ultra-low carbon methanol is positioned to become a key transitional fuel in the global decarbonization journey.
Market Overview
Marine bunker ultra-low carbon methanol encompasses bio-methanol derived from biomass, e-methanol produced using renewable hydrogen and captured CO2, and blue methanol from fossil sources with carbon capture. These fuels are compatible with existing vessel engines with minor modifications, offering a practical pathway for emission reduction. The liquid state of methanol simplifies storage, handling, and bunkering, making it more adaptable than alternatives like ammonia or hydrogen.
The adoption of ultra-low carbon methanol is further accelerated by the need to comply with international regulations, including the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) greenhouse gas strategy and the European Union’s Emissions Trading System. The market is defined by ongoing innovation in production, bunkering infrastructure, and engine technology to meet global shipping demands.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe are at the forefront of adoption. China leads the market, driven by an integrated industrial strategy, large-scale production facilities, and green methanol-ready ports. India focuses on decarbonizing coastal shipping and establishing green ports, while the USA leverages renewable energy sources and policy incentives to advance e-methanol adoption. Europe emphasizes sustainability in deep-sea shipping and green corridors, encouraging early adoption of low-carbon fuels in established shipping hubs.
Key Trends & Forecast
The marine bunker ultra-low carbon methanol market is shaped by several trends:
- Growth of Bio-Methanol and E-Methanol Production: Bio-methanol is currently the most commercially viable, while e-methanol promises deeper decarbonization for the long term.
- Container Ships as Early Adopters: Container lines, due to their predictable schedules and cargo owners’ emissions targets, are leading the transition to dual-fuel methanol-capable vessels.
- Deep-Sea Shipping Adoption: Long-distance shipping, which contributes the most to global maritime emissions, is the dominant application segment, incentivized by regulatory compliance and economic feasibility.
- Development of Green Shipping Corridors: Strategic shipping routes are being identified and equipped for consistent availability of low-carbon methanol, ensuring smooth fuel supply and operational continuity.
- Digital Certification and Fuel Tracking: Advancements in blockchain and digital monitoring ensure fuel provenance, providing transparency for regulators, charterers, and sustainability reporting.
Applications & End-Use Outlook
Ultra-low carbon methanol is deployed primarily in deep-sea shipping, but its use is expanding to container ships, tankers, bulk carriers, and passenger vessels. Its versatility supports coastal shipping, offshore support operations, and harbor services. The fuel’s adoption helps operators meet carbon intensity targets while providing stable operational performance, aligning with both regulatory and commercial sustainability goals.
Drivers and Restraints
The primary market driver is regulatory pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Charterer demands for greener logistics and the operational feasibility of methanol as a drop-in fuel further enhance adoption. Availability of dual-fuel engines, government incentives, and investments in methanol bunkering infrastructure support market growth.
Challenges include fragmented bunkering infrastructure, high initial capital expenditure, and the green premium associated with low-carbon methanol production. Additionally, scalability depends on sustainable feedstock and renewable energy inputs, which can vary regionally. Overcoming these barriers requires investment in infrastructure, partnerships, and strategic planning.
Competitive Landscape
Leading market players include Methanex Corporation, Proman AG, OCI N.V., EnerMech Methanol Partners, and Haldor Topsoe A/S. Companies compete through production capacity, technological innovation, strategic partnerships with shipping operators, and efforts to create integrated green methanol supply chains. The race focuses on establishing global bunkering networks and securing contracts with major container lines and deep-sea operators.
Country-Specific Insights
China’s focus on vertically integrated production and port upgrades is setting global standards for methanol bunkering. India prioritizes coastal shipping and green port initiatives to reduce domestic emissions. The USA leverages renewable energy for e-methanol production and policy-driven incentives to encourage adoption. Germany and Japan focus on sustainability and compliance in both coastal and international shipping.
Conclusion
The marine bunker ultra-low carbon methanol market is transforming global shipping, providing a feasible path to reduce carbon intensity while maintaining operational efficiency. By integrating bio-, e-, and blue methanol into vessel fleets, shipping companies can comply with evolving regulations, meet charterer sustainability demands, and advance toward net-zero goals. Continued investment in production, infrastructure, and vessel technology will be critical to scaling adoption, making low-carbon methanol a cornerstone of the maritime industry’s decarbonization strategy.
Browse Full Report – https://www.factmr.com/report/marine-bunker-ultra-low-carbon-methanol-market