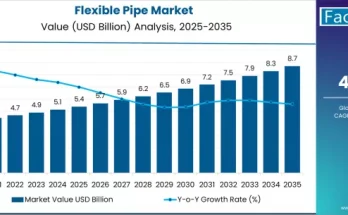
Landfill gas (LFG) is gaining prominence as a sustainable energy source, converting waste emissions into usable fuel and electricity. As urbanization increases and environmental regulations tighten, the landfill gas market is witnessing significant growth. Governments, utilities, and industries are recognizing the dual benefits of reducing greenhouse gas emissions while generating reliable energy from municipal and industrial waste.
Market Overview
Landfill gas is produced by the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste in landfills, primarily comprising methane and carbon dioxide. The global landfill gas market is expanding as technological advancements enhance gas recovery, purification, and utilization. Landfill gas systems can now support electricity generation, combined heat and power (CHP) operations, and renewable natural gas (RNG) for industrial and transportation applications. The market growth is fueled by a mix of environmental policies, economic incentives, and rising energy demands in urban centers worldwide.
Key Market Drivers
Regulatory Support and Environmental Policies
Governments worldwide are enforcing stringent regulations to reduce methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. Incentives such as carbon credits, tax benefits, and feed-in tariffs are motivating municipal and private landfill operators to implement LFG-to-energy projects. These policies align with global climate goals and promote the adoption of sustainable energy practices.
Renewable Energy Demand
As nations aim to diversify energy portfolios and reduce dependency on fossil fuels, landfill gas offers a stable, renewable, and scalable energy source. Utilities and independent power producers increasingly integrate LFG into their energy mix to provide baseload electricity and enhance grid stability, complementing intermittent renewables like wind and solar.
Rising Urbanization and Waste Generation
Urban expansion and population growth result in higher volumes of municipal solid waste, creating larger landfill sites and increased methane availability. With efficient collection and processing technologies, LFG can be harnessed effectively, converting environmental liabilities into economic assets.
Technological Advancements
Innovations in gas capture, purification, and monitoring have improved the efficiency and economic viability of landfill gas projects. Modern systems automate extraction, reduce operational costs, and ensure consistent gas quality, making landfill gas a reliable alternative for industrial and municipal energy applications.
Regional Insights
North America
North America is the market leader, driven by mature regulatory frameworks and a well-established waste management infrastructure. The United States, in particular, benefits from the Landfill Methane Outreach Program (LMOP), which supports hundreds of LFG energy projects nationwide. States like California, Texas, and Pennsylvania are pioneering LFG-to-energy applications, utilizing methane for electricity, vehicle fuel, and pipeline injection. Canada is also expanding biogas initiatives, guided by provincial policies.
Europe
Europe follows closely, with countries like the UK, Germany, and France implementing EU climate directives and circular economy policies. Feed-in tariffs, carbon pricing, and decarbonization targets are encouraging landfill gas adoption for electricity generation, biomethane blending, and combined heat and power applications. Eastern Europe is gradually improving waste management systems, creating new opportunities for landfill gas development.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is an emerging market, with China and Japan leading LFG adoption. China is investing heavily in waste-to-energy reforms and integrating landfill gas systems with industrial steam and fuel applications. South and Southeast Asia are seeing growth through pilot-scale projects and foreign development funding. Rising urban populations and waste generation present significant potential for LFG projects.
Latin America, Middle East & Africa
These regions are at an early stage of LFG adoption, with pilot-scale projects and utility-driven operations leading market penetration. Increasing environmental awareness and international collaborations are gradually encouraging landfill gas utilization.
Applications & End-Use Outlook
Electricity Generation
Electricity generation is the largest application segment in the landfill gas market. LFG provides stable, baseload power, which complements intermittent renewable energy sources. Many projects co-locate power generation with landfill sites to minimize transmission losses and optimize infrastructure. Internal combustion engines and turbines are commonly used to convert methane into electricity for local consumption or grid export.
Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
CHP applications allow landfill gas to simultaneously produce electricity and useful heat, improving overall energy efficiency. Municipalities and industrial plants leverage CHP systems to reduce energy costs while meeting sustainability objectives.
Renewable Natural Gas (RNG)
Landfill gas can be purified and injected into pipelines as RNG or compressed for vehicle fuel. This application is gaining popularity in the transportation sector as countries seek low-carbon alternatives to conventional natural gas and diesel.
Industrial Applications
Industrial facilities utilize LFG as a fuel for steam generation, heating processes, or as a feedstock for chemical production. This provides cost-effective energy solutions while contributing to corporate sustainability goals.
Country-Wise Insights
United States
The U.S. remains a leader due to mature infrastructure, strong regulatory backing, and active participation by private companies like Waste Management Inc. and Aria Energy. Federal incentives such as tax credits and renewable identification numbers (RINs) enhance project viability. The popularity of RNG in transportation is further driving LFG expansion.
United Kingdom
The UK market is expanding through ambitious decarbonization targets and circular economy mandates. LFG is increasingly used for grid injection and biomethane blending. Legacy projects are being modernized with improved automation and gas collection efficiency, complementing national renewable energy goals.
China
China’s growth is propelled by municipal waste reforms, industrial integration, and low-carbon initiatives. Major cities are investing in waste-to-energy infrastructure, combining LFG systems with environmental management programs. International cooperation and technological adoption are enhancing purification and compression processes, positioning China as a key global market.
Market Challenges
High Capital Expenditure
Initial investment costs for LFG projects are substantial, with long payback periods deterring smaller operators. Financing is often project-specific and depends on landfill size, waste composition, and gas yield.
Technical Complexities
Maintaining consistent gas quality and flow requires sophisticated monitoring and purification systems, which are labor-intensive and costly. Operational complexities can hinder efficiency and increase maintenance requirements.
Regulatory Variability
Emerging economies often lack standardized emission control laws, creating uncertainty for investors. Inconsistent policies can limit market confidence and slow adoption.
Competition from Other Renewables
Faster-to-deploy renewable sources like solar and wind can offer quicker returns and less complex infrastructure, making them more attractive in certain markets compared to landfill gas.
Key Trends
- Integration of LFG with renewable energy grids to provide baseload power.
- Expansion of RNG applications in transportation and industrial sectors.
- Technological innovations in gas purification, monitoring, and automation.
- Government incentives and policy frameworks supporting LFG adoption.
- Co-location of landfill gas projects with municipal and industrial waste sites for efficiency.
Future Outlook
The landfill gas market is poised for steady growth due to rising energy demand, stricter environmental regulations, and technological advancements. LFG is expected to play a significant role in transitioning toward low-carbon energy systems, complementing wind, solar, and other renewable sources. Emerging economies are likely to see increased adoption as infrastructure improves and sustainability initiatives expand.
Conclusion
Landfill gas represents a unique opportunity to turn waste into renewable energy while mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Its applications in electricity generation, CHP, RNG, and industrial energy make it a versatile and sustainable resource. With supportive policies, technological innovations, and increasing global awareness of environmental challenges, the landfill gas market is set for substantial expansion over the next decade, contributing to cleaner, more reliable, and diversified energy solutions worldwide.