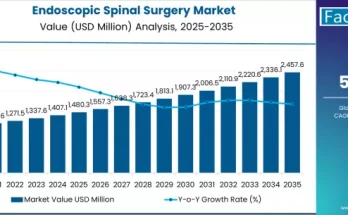
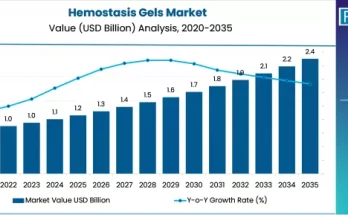
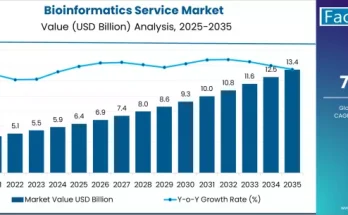
Decentralisation of clinical trials has been an ongoing topic of discussion and development. Decentralization makes clinical trials easier for patients by eliminating their need to travel. This approach has reduced drop-out routes and increased study-effectiveness and ultimately saves money. The COVID-19 pandemic has amplified the adoption of decentralized clinical trials while improving the patient and physician experience. Clinical-trial sponsors are continually putting emphasis to make clinical trials faster and to improve the patients and physicians.
Trial decentralization has emerged as a critical tool and it involves an increasing proportion of a trial’s activities to the patients rather than bringing patients to a trial site. Also, biopharma and biotech organizations are increasingly using decentralized or hybrid trial designs over traditional solutions. Moreover, biotech and biopharma companies are opting for decentralized or hybrid trial designs over traditional solutions. Patients are gaining more knowledge of alternative trial modes and have become more tech savvy. They are aware of technology modes such as televisits, remote monitoring, wearables and virtual sites to reduce delays.
Due to highly regulated healthcare market, decentralized trials have witnessed slow growth. However, regulators have been supporting decentralization. Sponsors expect to receive proper guidance from regulatory bodies before progressing with new technologies and processes.
Key trends in decentralized clinical trials market
Slow growth witnessed for nontech components – Decentralized clinical trials are not entirely tech-driven, there is a human touch to it. Besides this, pharma executives also indicate that keeping human element is important to maintain patient engagement. Besides this, Nontech driven DCT elements include synthetic controls and remote drug delivery. There are various nanotechnology approaches available in the market such as remote drug delivery and home nursing. Also, the uptake of these components is much slower than technology-based ones. During the covid-19 pandemic, growth rate of nontech decentralized clinical trials didn’t witness a surge. The slower uptake of nontech DCT is due to various challenges such as logistical and financial that involves training and hiring.
Clinical Research Organizations have been collaborating with sites to conduct clinical trials in a hybrid fashion – Remote visits are completed in the comfort of the patient’s home using mobile technology. Decentralized Clinical trials requires considerable adjustments to the traditional clinical trial rules. These carry uncontrolled risks such as variability of a patient’s technological experience. Also, decentralized clinical trials offer a lucrative opportunity in which transportation costs and logistics, access to remote areas are no longer barriers to the global expansion of clinical trials.
Benefits of decentralized clinical trials:
Meeting patients where they are: The concept of meeting patients where they are when conducting clinical trials has aimed to improve patient convenience and experience. Moreover, decentralization broadens the opportunity and also improves the trial access to reach a larger number and potentially a more diverse pool of patients. Decentralized clinical trials offer flexibility. Patients can record their data from any location such as work, while doing grocery shopping or at home.
Accurate picture of how a drug or device works in real life: CROs collecting data from a variety of environments gives clinical trial staff an accurate picture of how a drug or device works in real life. Also, this flexibility means that a patient’s health data might vary depending on the environment they are in. For instance, research staff could see differences in blood pressure because of stress from work or temperature fluctuations due to change in weather.
Reduction of Workload: Decentralization can also reduce the workload for trial investigators, since traditional site activities (such as drug administration, assessments, and data verification) can be performed remotely by others or by trial participants themselves.
Better reliability and accuracy of data: Collecting data using various technologies such as wearables, apps, and smartphones keep data organized and safe.
Challenges for decentralization:
Sponsors and service providers are implementing decentralized trials but they face uncertainties in technology. They face challenges due to industry’s long cycle times and conservativism.
- Decentralized trials can also serve participants who live hours away from research sites. But only those patients can have access to decentralization that have access to smartphones, WIFI. Participants also need to learn to operate wearable device or smartphone and computer applications. Also, this makes decentralized trials more complicated, since participants who have easy access to Wi-Fi and computers, may not feel comfortable using software.
- Decentralized clinical trials require technology that can transfer data from various technologies such as wearable technology or remote locations to research sites. Various sponsors and CROs are having trouble finding appropriate technology designed for decentralized trials.
- Apart from worrying about the cost of the technology, research organizations are also worried about how long it will take to implement a new technology. Also, clinical research professionals have busy schedules and limited time to learn new software programs.
- Patients sending their own data from home, work or school leads to higher risk that they might not use a device properly or record their data incorrectly. In this case, research sites need to give patients thorough training on how to use apps and wearables according to the study protocol. Also, some clinical research organizations even invest in devices that record data and send it to research site so that patients don’t need to worry about writing or typing the data incorrectly.
- Decentralized clinical trials allow the staff to collect patient data in a variety of environments. But the amount of data coming in can be overwhelming and if staff has to spend hours sifting through data points or transferring them between different systems, decentralized clinical trials could be very time-consuming than traditional ones.
Various pharmaceutical companies across the globe are offering decentralized clinical trials. Following is the list of pharmaceutical companies with proven success in this approach:
PPD: PPD is a reputed leader in the decentralized clinical trials space. Moreover, PPD has also collaborated with research organizations globally to assess upcoming trends in drug development and helps them to design and deploy remote clinical trials.
PRA Health Sciences: The company offers various services such as clinical research services, commercial positioning, laboratory services, medical imaging etc. The company is also committed to offer treatments to patients faster and more cost-effectively. Also, these offer a range of DCT solutions such as wearables, eConsent, virtual visits and videotelephony.
ICON:ICON is known for deploying decentralized clinical trials across multiple therapeutic areas offering a range of services that includes IRT, direct to patient contact, clinical supply management, in-home services, wearables and sensor management and remote monitoring.
Curebase: The company offers end-to-end clinical trial execution built on cutting-edge technology. The company provides the services to execute highly decentralized trials. This is used by many global pharmaceutical companies such as Gilead. Also, the company’s software technology and virtual staff enable clinical data collection from any of the locations.
Medidata: Medidata is one of the first companies to offer decentralising capabilities for both patient participation and study quality. Also, the company’s Trial Dial brand has been supporting organisations develop various protocols to support fully site-based and hybrid clinical studies.
Clinpal: The company’s end-to-end clinical research platform has been used for direct-to-patient studies. Moreover, the company’s solutions also include long-term extension and registry studies. This also includes questionnaire studies, patient recruitment and engagement.
THREAD: The company modernize clinical research with solutions such as patient engagement, econsent, digital recruitment, telehealth virtual visits, site data capture. Also, THREAD offers a range of DCT services including digital recruitment, patient engagement, econsent, eCOA, telehealth virtual visits, site data capture, sensors and analytics. They work to make clinical trials more efficient, flexible, and inclusive.
Parexel: Parexel offers both hybrid and fully virtual DCT solutions. The company has offered solutions for over 160 DCTs and have experience in over 200 patient engagement strategies that have been incorporated in the trials.