The textile industry is undergoing a major transformation with the adoption of bio-based coatings for technical textiles. These eco-friendly coatings, derived from renewable resources like plants and agricultural waste, offer a greener alternative to traditional petroleum-based coatings. Let’s explore why this shift is happening, the regions leading the way, and the latest trends and advancements in this field.
Bio-based coatings in the textile industry are innovative solutions derived from renewable biological resources, such as plants, algae, or microorganisms, aimed at providing functional enhancements to textiles while promoting sustainability. Unlike traditional petroleum-based coatings, bio-based alternatives utilize natural polymers like polysaccharides (e.g., starch, cellulose), proteins (e.g., soy protein, casein), and bio-based polymers (e.g., polylactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoates).
What are the advantages of bio-based coatings?
These coatings offer a range of functional properties, including water resistance, UV protection, antimicrobial activity, and flame retardancy. The primary advantage of bio-based coatings lies in their environmental benefits, as they reduce dependence on fossil fuels, lower carbon footprints, and often exhibit biodegradability, contributing to less environmental pollution. Additionally, they tend to contain fewer harmful chemicals, enhancing safety for both humans and ecosystems.
Applications of bio-based coatings span protective clothing, home textiles, industrial textiles, and sportswear, where they improve performance and durability. Despite challenges such as performance consistency, cost, and scalability, continued research and development in this field hold promise for advancing sustainable practices in the textile industry.
Bio-based coatings are finding applications across a diverse range of markets, driven by consumer demand for sustainable products. This diversification is expanding the reach and impact of bio-based technologies. For example:
- Adidas is a globally recognized sportswear company known for its innovative athletic apparel, footwear, and accessories. The company has introduced a line of sportswear that uses bio-based coatings to enhance moisture management and breathability. This line is designed for eco-conscious athletes who seek high-performance, sustainable gear.
- Patagonia is an outdoor apparel and equipment company that prioritizes environmental sustainability. The company incorporates bio-based coatings in its products to provide weather resistance and durability. Patagonia caters to adventurers who value eco-friendly and durable outdoor gear.
- Stella McCartney is a leading fashion brand that focuses on luxury textiles with a strong commitment to sustainability. The brand integrates bio-based coatings into its products, resonating with consumers who prioritize eco-friendly fashion choices. Stella McCartney drives innovation in textile coatings within the luxury fashion industry.
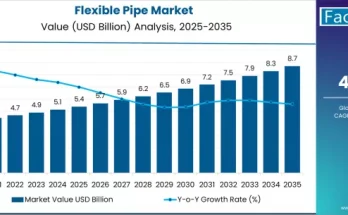
According to Fact.MR’s analysis, the global bio-based coating market stood at USD 11.5 Billion in 2022. It is further expected to surpass USD 28.50 Billion.
Why the Shift to Bio-Based Coatings?
The textile industry is one of the largest global contributors to pollution and carbon emissions—conventional coatings derived from petroleum lead to these issues. Bio-based coatings, made from renewable resources like plants and agricultural waste, offer a sustainable alternative. They reduce reliance on finite fossil fuels and minimize environmental impact throughout their lifecycle.
Governments worldwide are tightening environmental regulations to combat climate change and ecological degradation. Initiatives such as the EU’s Green Deal and stringent sustainability standards in the US are compelling industries to adopt cleaner technologies. Bio-based coatings align with these regulations by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting resource efficiency.
Moreover, there is a growing consumer awareness and preference for eco-friendly products. Modern consumers are increasingly informed about environmental issues and seek products that align with their values. This shift in consumer behavior is prompting companies to innovate and invest in sustainable solutions like bio-based coatings, ensuring they meet market demands for greener alternatives.
Recent advancements in biotechnology and materials science have significantly improved the performance and versatility of bio-based coatings. Manufacturers can now produce coatings that match or exceed the durability, flexibility, and protective properties of traditional petroleum-based coatings. This technological progress has expanded the application potential of bio-based coatings across various industries, from automotive to healthcare.
Latest Trends and Advancements
· Scientists are at the forefront of developing bio-based coatings using a variety of renewable sources. These materials not only provide environmental benefits but also enhance the performance characteristics of textiles.
· For instance, Companies like DuPont have been utilizing soy-based polymers to create coatings that are biodegradable and environmentally friendly. These coatings are used in automotive interiors and other applications requiring durable, eco-friendly finishes.
· Another example – Nature Works is a pioneer in producing Ingeo biopolymer, a polylactic acid (PLA) derived from corn. This material is used to create coatings for packaging and textiles, providing a compostable alternative to traditional plastics. Moreover, Researchers at companies such as Algix are developing algae-based coatings known for their UV resistance and antimicrobial properties. These coatings are particularly useful in outdoor textiles and marine applications, offering durability and protection against the elements.
- The development and commercialization of bio-based coatings are significantly accelerated through partnerships between universities, industries, and governments. These collaborations ensure that innovations are both practical and commercially viable. Examples include:
- BASF partners with universities around the world to research and develop new bio-based coatings. These collaborations focus on enhancing coating performance and sustainability, ensuring that new products meet industry standards and consumer expectations.
- Programs like the European Union’s Horizon 2020 fund research and innovation projects that include the development of bio-based materials. These initiatives bring together academic researchers and industrial partners to push the boundaries of sustainable coating technologies.
- Smart coatings represent a significant advancement in the textile industry, allowing materials to respond dynamically to environmental changes. This innovation enhances the functionality of textiles in various applications. Examples include:
- Outlast Technologies produces smart coatings that respond to temperature changes. These phase-change materials (PCMs) absorb, store, and release heat, providing thermal regulation in clothing and bedding.
- Devan Chemicals develops moisture-reactive coatings that adjust their properties based on humidity levels. These are particularly useful in performance sportswear, ensuring optimal comfort and performance.
- HeiQ Materials AG has created Viroblock, a smart coating that releases antimicrobial agents in response to microbial activity. This technology is widely used in medical textiles and personal protective equipment (PPE), providing enhanced protection against pathogens.
- The circular economy approach is gaining traction in the textile industry, with companies focusing on creating coatings that support recycling and biodegradability. This approach minimizes waste and promotes resource efficiency. Examples include:
- Covestro is developing coatings that can be easily separated from textiles during recycling processes. Their polyurethane-based coatings are designed to be compatible with existing recycling systems, facilitating the reuse of materials.
- Novamont produces Mater-Bi, a family of biodegradable and compostable bioplastics derived from renewable sources. These coatings are designed to break down naturally, reducing environmental impact and landfill waste.
- ECONYL® by Aquafil is an initiative that repurposes nylon waste into new textiles. The company uses bio-based coatings to enhance the durability and performance of these recycled materials, promoting a closed-loop system in the textile industry.