2036 Strategic Analysis of the Solid Sorbents for Direct Air Capture Market: Portfolio Priorities
The accelerating global drive toward net-zero emissions has placed Direct Air Capture (DAC) at the forefront of carbon removal technologies. Among DAC methods, solid sorbents have emerged as the most promising approach due to their high CO₂ selectivity, lower energy requirements, and scalable modular designs. By 2036, solid sorbent DAC is projected to evolve from pilot-scale demonstrations to fully commercial, infrastructure-integrated solutions, reshaping corporate portfolios and national decarbonization strategies. This analysis provides a data-driven assessment of market growth, portfolio priorities, adoption trends, and long-term demand projections.
Market Size and Growth Trajectory
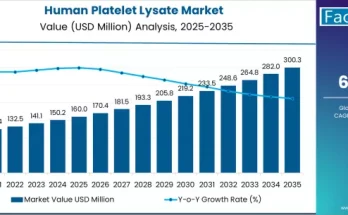
The global market for solid sorbents in DAC has demonstrated robust growth in the early 2020s, with more than 50% of total DAC deployments leveraging solid sorbents. The market is projected to expand from USD 475 million in 2026 to USD 1.63 billion by 2036, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 13%. This growth is fueled by the dual pressures of regulatory mandates and corporate net-zero commitments, as organizations increasingly purchase carbon removal credits to offset unavoidable emissions.
By 2030, cumulative CO₂ captured by solid sorbent DAC systems is expected to reach 15 million tons per year, rising to over 120 million tons per year by 2036. The adoption of high-capacity sorbents and efficiency-optimized DAC plants underpins this expansion, ensuring both economic viability and scalability.
Portfolio Priorities
1. Material Innovation
Investment portfolios are heavily focused on advanced sorbent materials that maximize CO₂ capture while minimizing energy consumption. The key categories include:
-
Amine-functionalized sorbents: Offering high selectivity at low partial pressures of CO₂, suitable for ambient air capture.
-
Zeolites: High structural stability and reusable over thousands of cycles, favored for continuous industrial applications.
-
Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Emerging as ultra-high surface-area materials capable of capturing CO₂ at ultra-low concentrations, though costs remain higher than amines or zeolites.
2. Energy Efficiency and Regeneration Optimization
Temperature Swing Adsorption (TSA) remains the dominant regeneration technology for solid sorbents, accounting for approximately 70% of commercial units. Reducing the energy required for sorbent regeneration is critical, as energy costs typically represent 40–50% of total DAC operating expenses. Leading portfolios prioritize sorbents capable of low-temperature regeneration, leveraging waste heat from nearby industrial processes or renewable electricity to reduce carbon intensity and operational expenditure.
3. Modular and Scalable System Design
The modularization of DAC units allows for phased deployment and risk mitigation. Currently, 60–65% of new DAC installations adopt containerized or modular formats. These systems enable scalability from 5,000-ton annual capture units to 100,000-ton commercial-scale facilities, aligning capital expenditure with measurable carbon removal outcomes.
Adoption Trends
Policy-Driven Early Adoption
Government incentives remain pivotal. By 2030, cumulative funding and tax incentives for carbon removal technologies are expected to exceed USD 5 billion globally, driving accelerated adoption in North America and Europe. Adoption in these regions represents roughly 75% of the early-market DAC deployments, while Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are rapidly scaling pilot projects to achieve industrial capacity by 2035.
Transition from Pilot to Commercial Scale
Early DAC plants captured less than 10,000 tons of CO₂ annually, but commercial plants now target 100,000–500,000 tons per year, a 10–50x increase in scale. By 2036, large-scale facilities are projected to account for over 80% of global solid sorbent DAC capacity, reflecting technology maturation, cost reductions, and integration with industrial clusters.
Diversification of Applications
Solid sorbent DAC adoption is expanding beyond geological sequestration. Applications now include:
-
Synthetic fuels: DAC-derived CO₂ used to produce low-carbon synthetic hydrocarbons, projected to consume 30–35% of captured CO₂ by 2036.
-
Building materials: Carbon-mineralized concrete products, projected to account for 20% of CO₂ utilization.
-
Chemical feedstocks: Providing CO₂ as a raw material for specialty chemicals and polymers, representing 15–20% of usage.
This diversification not only increases revenue potential but also stabilizes demand, mitigating reliance on a single sequestration pathway.
Competitive Landscape
The solid sorbent DAC market is characterized by a mix of climate-tech innovators and established industrial players. Strategic positioning emphasizes:
-
Vertical integration: Combining sorbent development, plant engineering, and carbon credit monetization to secure predictable cash flows.
-
Strategic partnerships: Collaborations with energy providers, EPC contractors, and industrial CO₂ end-users to reduce deployment risks.
-
R&D pipelines: Focused on next-generation sorbents capable of >10% higher capture efficiency, 10–15% lower regeneration energy, and durability exceeding 5,000 cycles.
By 2036, a handful of leading companies are expected to capture 60–70% of the commercial market, reflecting economies of scale, proprietary sorbent technologies, and robust deployment networks.
Demand Outlook
Demand drivers for solid sorbent DAC through 2036 include:
-
Compliance and Voluntary Carbon Markets – By 2036, over 200 million tons of CO₂ removal per year are projected to be mandated globally, with solid sorbents expected to supply 50–60% of this demand.
-
Cost Reduction Trajectory – Solid sorbent DAC costs are projected to decline from $250–$300 per ton today to under $100 per ton by 2036, driven by material innovation, modular scaling, and energy integration.
-
Geographic Expansion – While North America and Europe dominate current adoption, Asia-Pacific is projected to grow at 15–20% CAGR, driven by industrial cluster deployment and government incentives.
By 2036, solid sorbent DAC is expected to be a foundational component of national decarbonization strategies, contributing significantly to climate goals while creating new industrial value chains.
Browse Full Report : https://www.factmr.com/report/solid-sorbents-for-direct-air-capture-market
Strategic Implications
The period leading to 2036 represents a decisive window for stakeholders in the solid sorbent DAC market. Portfolio priorities should focus on:
-
Investing in high-performance sorbents with long-term durability and low regeneration energy.
-
Expanding modular, scalable deployment strategies to align capital with measurable CO₂ removal.
-
Securing strategic partnerships and offtake agreements to ensure predictable market capture.
Adoption trends indicate a clear trajectory from experimental pilots to fully commercial facilities, with diversified applications supporting long-term demand. By integrating technological, economic, and policy considerations, solid sorbents are positioned to become a critical pillar in the global carbon removal economy by 2036.