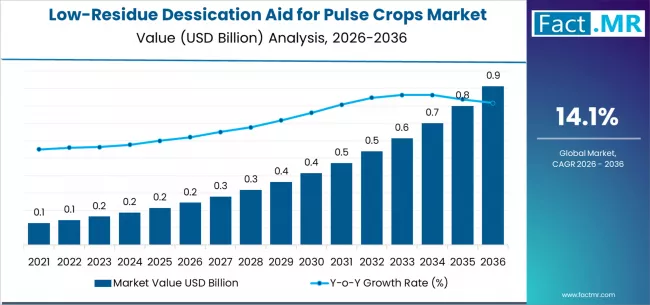
Pulse crops such as lentils, chickpeas, peas, and beans play a critical role in global food security due to their high protein content and soil-enhancing properties. As agricultural practices modernize, farmers are increasingly adopting solutions that improve harvest efficiency while maintaining crop quality and safety. Low-residue dessication aids for pulse crops have emerged as an important tool in this transition, enabling uniform crop drying and timely harvesting with minimal chemical residue. The growing emphasis on sustainable farming, residue-compliant produce, and export quality standards is shaping the development of this specialized agricultural input market.
Market Overview
The low-residue dessication aid for pulse crops market focuses on products designed to accelerate plant dry-down prior to harvest while leaving minimal residues on harvested grains. These solutions help farmers manage uneven crop maturity, reduce moisture levels, and minimize harvest losses caused by weather variability. Unlike conventional chemical dessicants, low-residue formulations are developed to comply with strict food safety and residue regulations, making them suitable for both domestic consumption and international trade.
Adoption of these products is increasing as pulse growers seek to optimize harvest timing, improve grain quality, and reduce dependency on mechanical drying. The market includes chemical-based and biologically derived solutions, with manufacturers continuously refining formulations to balance efficacy, crop safety, and environmental impact.
Regulatory and Sustainability Considerations
Regulatory frameworks play a central role in shaping the low-residue dessication aid market. Governments and food safety authorities impose maximum residue limits on agricultural produce, particularly for export-oriented crops such as pulses. Low-residue dessication aids are developed to meet these standards, allowing farmers to comply with regulations while maintaining productivity.
Sustainability is another key consideration driving market adoption. Pulse crops are often promoted as environmentally friendly due to their nitrogen-fixing capabilities, and growers are increasingly expected to follow sustainable input practices. Low-residue dessication aids align well with integrated crop management and sustainable agriculture initiatives by reducing chemical load in the food chain and minimizing environmental impact.
Regional Insights
North America represents a prominent market for low-residue dessication aids, supported by large-scale pulse production and advanced farming practices. Farmers in the region prioritize harvest efficiency and quality consistency, making low-residue solutions an attractive option for managing pre-harvest conditions.
Europe also demonstrates strong demand, driven by strict regulatory oversight and consumer preference for residue-compliant agricultural products. The region’s focus on sustainable farming and traceability further supports the adoption of low-residue dessication technologies.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as an important growth area, supported by expanding pulse cultivation and increasing awareness of modern agronomic practices. Governments and agricultural organizations in this region are promoting improved crop management techniques to enhance yields and export competitiveness, creating opportunities for low-residue dessication aids.
Key Trends and Market Outlook
One of the major trends in this market is the shift toward safer and more targeted crop dessication solutions. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop formulations that act selectively on plant tissues, ensuring effective drying without compromising seed quality or soil health.
Another notable trend is the integration of dessication aids into precision agriculture systems. Farmers are increasingly using data-driven tools to determine optimal application timing, dosage, and crop conditions. Low-residue dessication aids complement these practices by offering predictable performance and reduced risk of residue violations.
There is also growing interest in bio-based and low-toxicity alternatives. While chemical dessicants remain widely used, demand for environmentally friendly and residue-minimized products is encouraging innovation in biological and plant-derived solutions.
Applications and End-Use Outlook
Low-residue dessication aids are primarily used in the cultivation of pulse crops such as dry peas, lentils, chickpeas, and beans. These crops often exhibit uneven maturation, which can complicate harvesting and affect grain quality. Dessication aids help synchronize crop dry-down, enabling efficient mechanical harvesting and reducing grain losses.
Commercial farms and contract growers are key end users, particularly those supplying export markets where residue compliance is critical. Seed producers also utilize low-residue dessication aids to ensure seed quality and maintain germination potential.
In addition, farmer cooperatives and agribusiness service providers play an important role in promoting adoption by offering technical guidance, application services, and integrated crop management solutions.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The competitive landscape of the low-residue dessication aid market includes established agrochemical companies and specialized agricultural input suppliers. Competition is driven by formulation effectiveness, regulatory compliance, and compatibility with different pulse crop varieties.
Innovation remains a key differentiator, with companies focusing on improving product stability, application flexibility, and crop-specific performance. Partnerships with agricultural research institutions and extension services help manufacturers validate product performance under diverse growing conditions.
Conclusion
The low-residue dessication aid for pulse crops market is gaining importance as farmers balance productivity, sustainability, and food safety requirements. By enabling efficient harvesting with minimal residue concerns, these products support modern pulse cultivation practices and help meet stringent regulatory and market demands. As global consumption of pulses continues to rise and agricultural standards evolve, low-residue dessication aids are expected to play a vital role in enhancing crop quality, harvest efficiency, and sustainable farming outcomes.
Browse Full Report –
Low-Residue Dessication Aid for Pulse Crops Market: Advancing Efficient and Sustainable Harvesting
Pulse crops such as lentils, chickpeas, peas, and beans play a critical role in global food security due to their high protein content and soil-enhancing properties. As agricultural practices modernize, farmers are increasingly adopting solutions that improve harvest efficiency while maintaining crop quality and safety. Low-residue dessication aids for pulse crops have emerged as an important tool in this transition, enabling uniform crop drying and timely harvesting with minimal chemical residue. The growing emphasis on sustainable farming, residue-compliant produce, and export quality standards is shaping the development of this specialized agricultural input market.
Market Overview
The low-residue dessication aid for pulse crops market focuses on products designed to accelerate plant dry-down prior to harvest while leaving minimal residues on harvested grains. These solutions help farmers manage uneven crop maturity, reduce moisture levels, and minimize harvest losses caused by weather variability. Unlike conventional chemical dessicants, low-residue formulations are developed to comply with strict food safety and residue regulations, making them suitable for both domestic consumption and international trade.
Adoption of these products is increasing as pulse growers seek to optimize harvest timing, improve grain quality, and reduce dependency on mechanical drying. The market includes chemical-based and biologically derived solutions, with manufacturers continuously refining formulations to balance efficacy, crop safety, and environmental impact.
Regulatory and Sustainability Considerations
Regulatory frameworks play a central role in shaping the low-residue dessication aid market. Governments and food safety authorities impose maximum residue limits on agricultural produce, particularly for export-oriented crops such as pulses. Low-residue dessication aids are developed to meet these standards, allowing farmers to comply with regulations while maintaining productivity.
Sustainability is another key consideration driving market adoption. Pulse crops are often promoted as environmentally friendly due to their nitrogen-fixing capabilities, and growers are increasingly expected to follow sustainable input practices. Low-residue dessication aids align well with integrated crop management and sustainable agriculture initiatives by reducing chemical load in the food chain and minimizing environmental impact.
Regional Insights
North America represents a prominent market for low-residue dessication aids, supported by large-scale pulse production and advanced farming practices. Farmers in the region prioritize harvest efficiency and quality consistency, making low-residue solutions an attractive option for managing pre-harvest conditions.
Europe also demonstrates strong demand, driven by strict regulatory oversight and consumer preference for residue-compliant agricultural products. The region’s focus on sustainable farming and traceability further supports the adoption of low-residue dessication technologies.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as an important growth area, supported by expanding pulse cultivation and increasing awareness of modern agronomic practices. Governments and agricultural organizations in this region are promoting improved crop management techniques to enhance yields and export competitiveness, creating opportunities for low-residue dessication aids.
Key Trends and Market Outlook
One of the major trends in this market is the shift toward safer and more targeted crop dessication solutions. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop formulations that act selectively on plant tissues, ensuring effective drying without compromising seed quality or soil health.
Another notable trend is the integration of dessication aids into precision agriculture systems. Farmers are increasingly using data-driven tools to determine optimal application timing, dosage, and crop conditions. Low-residue dessication aids complement these practices by offering predictable performance and reduced risk of residue violations.
There is also growing interest in bio-based and low-toxicity alternatives. While chemical dessicants remain widely used, demand for environmentally friendly and residue-minimized products is encouraging innovation in biological and plant-derived solutions.
Applications and End-Use Outlook
Low-residue dessication aids are primarily used in the cultivation of pulse crops such as dry peas, lentils, chickpeas, and beans. These crops often exhibit uneven maturation, which can complicate harvesting and affect grain quality. Dessication aids help synchronize crop dry-down, enabling efficient mechanical harvesting and reducing grain losses.
Commercial farms and contract growers are key end users, particularly those supplying export markets where residue compliance is critical. Seed producers also utilize low-residue dessication aids to ensure seed quality and maintain germination potential.
In addition, farmer cooperatives and agribusiness service providers play an important role in promoting adoption by offering technical guidance, application services, and integrated crop management solutions.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The competitive landscape of the low-residue dessication aid market includes established agrochemical companies and specialized agricultural input suppliers. Competition is driven by formulation effectiveness, regulatory compliance, and compatibility with different pulse crop varieties.
Innovation remains a key differentiator, with companies focusing on improving product stability, application flexibility, and crop-specific performance. Partnerships with agricultural research institutions and extension services help manufacturers validate product performance under diverse growing conditions.
Conclusion
The low-residue dessication aid for pulse crops market is gaining importance as farmers balance productivity, sustainability, and food safety requirements. By enabling efficient harvesting with minimal residue concerns, these products support modern pulse cultivation practices and help meet stringent regulatory and market demands. As global consumption of pulses continues to rise and agricultural standards evolve, low-residue dessication aids are expected to play a vital role in enhancing crop quality, harvest efficiency, and sustainable farming outcomes.
Browse Full Report – https://www.factmr.com/report/low-residue-dessication-aid-for-pulse-crops-market