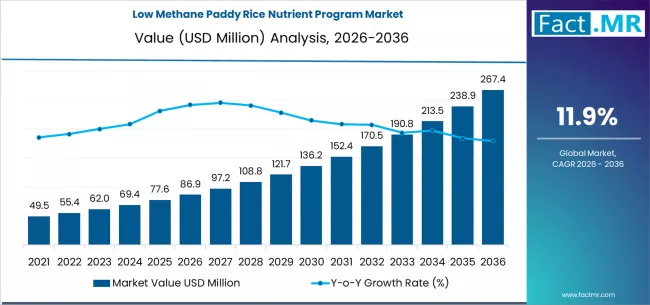
The global low methane paddy rice nutrient program market is set for strong expansion over the next decade, driven by rising climate change mitigation efforts, sustainable agriculture initiatives, and increasing pressure to reduce methane emissions from rice cultivation. According to a new analysis by Fact.MR, the market is projected to grow from USD 86.85 million in 2026 to USD 267.35 million by 2036, reflecting an impressive CAGR of 11.9% during the forecast period.
This rapid growth highlights the rising adoption of climate-smart nutrient management solutions designed to reduce methane emissions from flooded paddy fields—one of agriculture’s largest sources of greenhouse gases—while maintaining or improving crop yields.
The increasing integration of environmentally friendly fertilizers, soil amendments, and nutrient optimization technologies is accelerating adoption across both developed and emerging agricultural economies.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/low-methane-paddy-rice-nutrient-program-market
Strategic Market Drivers
Climate Change Mitigation and Methane Reduction Goals
Methane emissions from rice paddies contribute significantly to global greenhouse gas inventories. Governments, international climate organizations, and sustainability-focused agribusinesses are actively promoting low methane nutrient programs as a practical solution to reduce emissions without compromising food security.
Global climate commitments under frameworks such as net-zero agriculture, carbon neutrality goals, and sustainable development targets are driving policy-backed adoption of methane-reducing rice cultivation practices.
Sustainable Agriculture and Precision Farming Adoption
The shift toward sustainable and regenerative agriculture is accelerating the use of advanced nutrient formulations that optimize soil chemistry, regulate microbial activity, and reduce anaerobic methane generation in flooded fields.
Integration with precision farming technologies, including soil monitoring, controlled-release nutrients, and data-driven fertilizer application, is further enhancing program effectiveness and farmer acceptance.
Rising Demand for Low-Carbon Rice Supply Chains
Food companies, exporters, and retailers are increasingly demanding low-carbon and sustainably produced rice to meet ESG commitments and consumer expectations. Low methane paddy rice nutrient programs support traceable, environmentally responsible supply chains, increasing their attractiveness across global markets.
Carbon credit monetization opportunities linked to methane reduction are also encouraging large-scale adoption among commercial rice producers.
Government Incentives and Agricultural Policy Support
Subsidies, pilot programs, and public-private partnerships promoting emission-reducing agricultural inputs are accelerating market penetration. Governments across Asia, Europe, and North America are supporting nutrient innovation to reduce agriculture’s climate footprint.
Regional Growth Highlights
Asia-Pacific: Dominant Rice-Producing Region
Asia-Pacific leads the global market due to its dominance in rice cultivation. China, India, Vietnam, Indonesia, Thailand, and Bangladesh are key adopters as governments and NGOs push methane mitigation strategies in high-emission rice-growing regions.
Large-scale demonstration projects and farmer education programs are accelerating adoption across smallholder and commercial farms.
Europe: Sustainability and Climate Policy Leadership
European markets are adopting low methane rice nutrient programs through research-driven initiatives and climate-focused agricultural policies. Although rice cultivation is limited, Europe plays a critical role in technology development, innovation, and export of nutrient solutions.
North America: Innovation and Carbon Farming Growth
The U.S. market is expanding through carbon farming programs, sustainable food sourcing initiatives, and climate-resilient agriculture research. Partnerships between agritech firms and rice producers are strengthening market growth.
Emerging Markets: Strong Long-Term Potential
Latin America, Africa, and parts of the Middle East are witnessing growing interest due to:
- Expansion of irrigated rice farming
- Climate adaptation funding
- International development programs targeting methane reduction
Market Segmentation Insights
By Program Type
- Nutrient-Based Methane Reduction Programs – Dominant segment using optimized fertilizers and soil conditioners
- Microbial & Bio-based Solutions – Fast-growing due to eco-friendly profiles
- Integrated Nutrient & Water Management Programs – High adoption in precision agriculture
By Application
- Conventional Flooded Rice Cultivation – Largest segment
- Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) Systems – High-growth segment
- Organic and Sustainable Rice Farming – Rising demand
By End User
- Smallholder Farmers – Large volume adoption supported by subsidies
- Commercial Rice Producers – Fastest growth driven by ESG compliance
- Government & NGO Programs – Strategic market drivers
Challenges Impacting Market Growth
Limited Farmer Awareness and Training
Adoption is constrained in some regions due to lack of technical knowledge and limited access to extension services.
Higher Initial Costs
Advanced nutrient formulations and monitoring systems can be costlier than conventional fertilizers, particularly for smallholder farmers without subsidies.
Measurement and Verification Complexity
Accurately measuring methane reduction outcomes requires specialized tools, adding complexity to program implementation and carbon credit validation.
Competitive Landscape
The low methane paddy rice nutrient program market is fragmented but innovation-driven, with companies focusing on:
- Advanced nutrient chemistry
- Bio-based and microbial formulations
- Carbon credit-linked solutions
- Farmer education and digital advisory platforms
Key Players Operating in the Market
- Global agri-input manufacturers
- Sustainable fertilizer producers
- Agritech startups specializing in methane reduction
- Research-backed agricultural solution providers
Recent Developments
- 2024: Expansion of pilot methane-reduction rice programs across Asia supported by climate finance initiatives
- 2023: Introduction of bio-based nutrient solutions reducing methane emissions by over 30% in field trials
- 2022: Collaboration between agritech firms and food brands to scale low-carbon rice supply chains
Future Outlook: Climate-Smart Rice Farming Takes Center Stage
The coming decade will witness rapid transformation in rice cultivation practices, driven by:
- Global methane reduction commitments
- Expansion of carbon farming and ESG-linked agriculture
- Innovation in nutrient science and microbial soil management
- Increased demand for sustainable and traceable rice
As agriculture becomes central to climate action strategies, the low methane paddy rice nutrient program market is positioned for robust, long-term growth through 2036, offering a scalable solution to reduce emissions while safeguarding global food security.