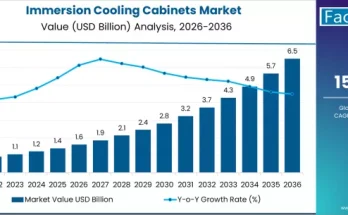
The global Semiconductor Epoxy MOF (Metal–Organic Framework) Emissions Capture Market is emerging as a critical enabler of sustainable semiconductor manufacturing. MOF-enhanced epoxy systems are increasingly deployed to capture volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides (NOx), methane, and other hazardous air pollutants released during epoxy resin processing, wafer fabrication, and curing operations. These emissions are under rising regulatory and investor scrutiny as semiconductor fabs expand globally.
The sector is transitioning from early adoption to accelerated commercialization, driven by growing awareness of environmental impact and the demand for advanced emissions control solutions. This positions semiconductor-specific MOF epoxy systems as a specialized but strategically important sub-segment within the broader metal–organic frameworks market.
2. Key Market Drivers
a. Regulatory Pressure and Environmental Compliance
Semiconductor manufacturing is subject to stringent air-quality regulations, particularly in major production hubs such as the U.S., EU, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan. Regional air-quality rules targeting VOCs and NOx increase compliance costs for fabs that rely on conventional abatement technologies. MOF-enhanced epoxy capture systems offer higher selectivity and adsorption efficiency than traditional methods, making them attractive for next-generation compliance strategies.
b. Expansion of Semiconductor Manufacturing Capacity
Global semiconductor capital expenditure remains structurally high due to demand from AI, automotive electronics, and advanced packaging. Each new fab increases epoxy usage in encapsulation, die attach, and protective coatings, directly expanding the addressable emissions capture market. Asia-Pacific and North America are identified as the fastest-growing regions due to fab localization strategies and supply-chain resilience initiatives.
c. Performance Advantages of Zirconium-Based MOFs
Zirconium-based MOFs dominate the market due to their high thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation under semiconductor process conditions. These properties reduce lifecycle costs and downtime, supporting faster adoption by high-volume manufacturers.
3. Disruption Signals and Technology Inflection Points
a. Integration of MOF Nanocomposites
Recent advances in MOF nanocomposites indicate a shift from passive adsorption toward multifunctional systems that combine capture with catalytic degradation or regeneration capabilities. Hybrid MOF–polymer architectures offer improved durability and adsorption kinetics, signaling potential step-changes in system efficiency over the next decade.
b. Cost Compression and Scale Effects
Historically, the high cost of MOF synthesis constrained adoption. However, process improvements and scale-up across the broader MOF market are expected to lower unit costs and accelerate penetration in semiconductor fabs.
c. Convergence with Carbon Capture and ESG Markets
While semiconductor epoxy MOF systems primarily target localized emissions, they align strategically with the expanding global carbon capture and removal ecosystem. This convergence reinforces investor and policy support for advanced capture technologies.
4. Competitive and Value-Chain Dynamics
The value chain spans MOF material developers, epoxy formulators, emissions-control system integrators, and semiconductor OEMs. Competitive differentiation increasingly depends on:
-
Capture efficiency at low concentration thresholds
-
Regenerability and system lifespan
-
Compatibility with existing fab exhaust and process flows
-
Regulatory certification and audit readiness
Epoxy resin processing and curing applications currently account for a substantial portion of total market demand, making them the primary focus for near-term innovation and partnerships.
5. Industry Scenarios (2026–2036)
Base-Case Scenario (Most Likely):
Regulatory tightening proceeds steadily, semiconductor capacity expands as forecast, and MOF costs decline incrementally. Market growth continues steadily, driven by compliance demand and expanding fab infrastructure.
Accelerated Adoption Scenario:
Stricter air-quality enforcement and faster MOF cost reductions drive earlier-than-expected replacement of legacy abatement systems. Adoption accelerates, and the market reaches new milestones before 2036.
Constraint Scenario:
Supply-chain disruptions or slower regulatory enforcement delay adoption. Growth moderates, with fabs prioritizing incremental upgrades over full system replacement.
6. Strategic Implications for Executives
-
For semiconductor manufacturers: Early adoption of MOF epoxy capture systems can reduce long-term compliance risk and improve ESG performance metrics.
-
For materials and chemicals firms: Differentiation through durability, regeneration, and integration capabilities will be critical as competition intensifies.
-
For investors: The segment offers exposure to both semiconductor growth and environmental technology tailwinds, with defensible demand driven by regulation rather than discretionary spending.
Browse Full Report : https://www.factmr.com/report/semiconductor-epoxy-mof-emissions-capture-market
Conclusion
The semiconductor epoxy MOF emissions capture market is transitioning into a strategically essential component of sustainable semiconductor manufacturing. Market trends indicate robust, regulation-anchored growth over the next decade, with technological innovation and policy alignment acting as reinforcing forces. Firms that position early in this niche, yet rapidly scaling, market are likely to capture disproportionate long-term value as environmental compliance becomes inseparable from semiconductor competitiveness.