Strategic Analysis of the Huntington’s Disease Treatment Market to 2036
1. Market Overview and Growth Trajectory
The global Huntington’s Disease (HD) treatment market is positioned for significant expansion over the next decade. In 2025, it is estimated at approximately USD 724.6 million, and forecasts suggest it will reach USD 1,543.9 million by 2035, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of ~7.8% between 2025–2035.
This growth is occurring against a backdrop of:
-
A rise in HD diagnosis due to expanding genetic testing and awareness.
-
Robust pipeline activity for disease‑modifying therapies leveraging cutting‑edge genetic technology.
-
Enhanced regulatory frameworks offering fast‑track and orphan drug pathways.
While prevalence remains low compared with other neurodegenerative disorders, the unmet clinical need, significant morbidity, and high lifetime disease burden create strong incentives for innovative therapies and market growth.
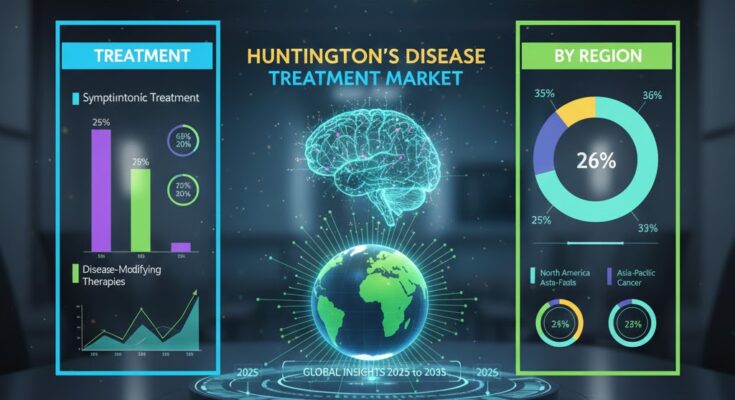
2. Portfolio Priorities: From Symptomatic to Disease‑Modifying Therapies
Symptomatic Treatments, the Current Mainstay
Historically, the HD landscape has been dominated by symptomatic management—particularly for chorea (involuntary movements), psychiatric manifestations, and cognitive decline. These medications improve quality of life but do not alter the underlying disease course. Common pharmacologic classes include:
-
VMAT2 inhibitors such as tetrabenazine derivatives targeting chorea.
-
Antipsychotics and antidepressants for mood and behavior symptoms.
-
Supportive interventions like occupational or speech therapy.
Symptomatic therapies currently make up approximately 65% of the market, indicating entrenched demand.
Emergence of Disease‑Modifying Therapies (DMTs)
The most important strategic shift through 2036 will be moving from palliative care toward disease‑modifying approaches that attack the genetic basis of Huntington’s:
A. Genetic Silencing Technologies
-
Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs): ASOs bind mutant huntingtin mRNA to reduce production of the toxic huntingtin protein.
-
RNA interference (RNAi) approaches aim for similar gene suppression.
These approaches are central to many late‑stage clinical programs and represent a major portfolio priority for biopharma innovators.
B. Gene Therapy Advances
Gene therapies offer potential one‑time or infrequently administered treatments that could significantly slow disease progression or modify natural history. Recent clinical results have shown up to 75% reduction in disease progression over three years, a landmark efficacy signal. This represents a transformative candidate in the HD pipeline.
C. Novel Modulators and Emerging Platforms
Beyond gene silencing and editing, stem cell therapy, epigenetic modulators, and targeted small molecules are advancing preclinically and in early clinical studies. These expandable portfolios will help pharmaceutical companies diversify risk and build differentiated offerings.
3. Adoption Trends and Market Dynamics
Regulatory and Reimbursement Trends
Regulators are evolving policies to support rare disease drug development, offering priority review, accelerated pathways, and orphan designations. These expedite access and incentivize investment in clinical development.
However, regulatory feedback can also create volatility. Some clinical dataset submissions have been deemed inadequate for approval, slowing expected launch timelines and highlighting the importance of robust trial design and stakeholder engagement.
Diagnostics and Early Detection
HD diagnosis historically lagged due to limited access to genetic testing. However, expanding genomic screening combined with awareness campaigns is increasing identification rates, particularly in North America and Europe. Improved detection enhances treatment initiation and eligibility for clinical trials, accelerating therapy adoption.
Real‑World Evidence and Biomarker Integration
Biomarkers like neurofilament light chain (NfL) are gaining traction as surrogate endpoints in trials, enabling faster go/no‑go decisions for development programs. This integration improves pipeline throughput and reduces development risk, key for both investors and regulatory authorities.
4. Competitive Landscape and Strategic Priorities
Key Players and Investments
Although the HD market remains smaller in absolute revenue than many chronic disease categories, the competitive landscape is intensifying, with major and emerging players investing in innovation:
-
Large pharmaceutical firms are building portfolios in genetic therapies and targeted approaches.
-
Smaller biotech innovators are driving breakthroughs, and strategic partnerships help de‑risk R&D costs and broaden development capabilities.
Strategic Alliances and Ecosystem Engagement
Academic partnerships, biotech collaborations, and patient advocacy involvement are essential for accelerating adoption. These alliances help:
-
Improve trial enrollment in rare disease populations.
-
Provide longitudinal real‑world data.
-
Influence payer and policy dialogues, which are critical for long-term market access and sustainable reimbursement.
5. Regional Market Outlook and Demand Drivers
North America
This region remains the largest and most mature HD therapy market due to:
-
Advanced healthcare infrastructure.
-
High rates of genetic testing and disease awareness.
-
Strong clinical trial networks and regulatory support.
Significant pipeline activity centered in the U.S. is likely to drive early adoption of novel therapies as they get approved.
Europe
Europe is marked by broad healthcare access and policy initiatives for rare diseases, supporting stable market growth. National rare disease frameworks facilitate diagnosis and expand treatment availability.
Asia‑Pacific
Emerging as one of the fastest growing regions, especially in China and South Korea, Asia-Pacific benefits from:
-
Increasing healthcare expenditures.
-
Growing genetic research investment.
-
Rising public awareness and expanding diagnostic services.
These trends suggest future unmet needs will increasingly be addressed across broader geographies.
6. Future Demand and Outlook to 2036
Market Expansion
Between 2025–2036, the Huntington’s Disease treatment market is forecast to expand well beyond symptomatic care, underpinned by:
-
Shifts toward disease‑modifying treatments.
-
Broader diagnostic reach.
-
Enhanced regulatory and payer support.
Projections place the market at significant growth through 2035 (doubling or more), with continued acceleration into 2036 and beyond as innovative therapies enter commercialization.
Demand Drivers
-
Growing diagnosed patient base due to genetic screening.
-
Clinical validation of DMTs that alter disease progression.
-
Healthcare system readiness to adopt and reimburse advanced treatments.
-
Expansion of digital health and remote monitoring to support chronic care models.
Browse Full Report : https://www.factmr.com/report/huntingtons-disease-treatment-market
Conclusion
The Huntington’s Disease treatment market is transitioning from a symptomatic care model to a cutting‑edge genetic therapeutic landscape. The strategic imperative for companies involves balancing near-term adoption of symptomatic therapies with long-term investments in disease-modifying portfolios. Regulatory navigation, early diagnosis, and stakeholder partnerships will be pivotal through 2036. With multiple promising clinical entrants and increasing global healthcare engagement, the HD market is poised for transformative growth that could dramatically improve patient outcomes and reshape competitive priorities in the neurodegenerative therapy sphere.