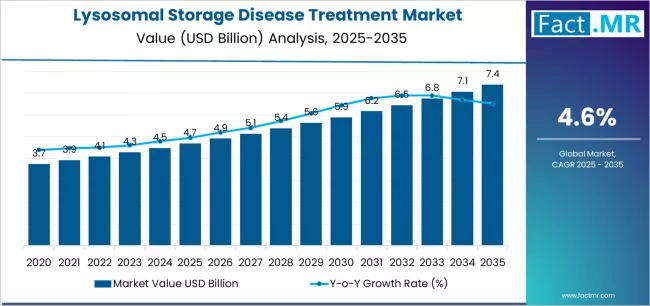
The lysosomal storage disease (LSD) treatment market is entering a dynamic phase of innovation and commercialization as advances in molecular diagnostics, enzyme technologies, and gene therapies broaden therapeutic options for a set of rare, genetically driven disorders. LSDs including Gaucher disease, Fabry disease, Pompe disease, and mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) collectively affect tens of thousands of patients worldwide. Historically underserved due to small patient populations and complex biology, this therapeutic area is now attracting sustained R&D investment, regulatory incentives for orphan products, and greater attention from specialist clinicians and patient advocacy groups.
Quick Stats (qualitative)
-
Primary Therapeutic Modalities: Enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs), substrate reduction therapies (SRTs), pharmacological chaperones, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), and gene therapies.
-
Key Indications: Gaucher, Fabry, Pompe, MPS I–VII subtypes, and rarer enzyme-deficient disorders.
-
Market Drivers: Improved diagnostics & newborn screening, regulatory orphan incentives, breakthroughs in gene-editing and AAV-based delivery, stronger patient advocacy, and expanded reimbursement frameworks in developed markets.
-
Principal Challenges: High treatment costs, limited patient numbers per indication, blood–brain barrier delivery for CNS forms, immune responses, and complex manufacturing.
To access the complete data tables and in-depth insights, request a Discount On The Report here: https://www.factmr.com/connectus/sample?flag=S&rep_id=12211
Market Drivers & Opportunities
1. Diagnostic Advances & Earlier Detection
Wider adoption of newborn screening, whole-exome/genome sequencing, and improved biomarker panels are identifying affected infants and asymptomatic carriers earlier. Earlier diagnosis increases eligibility for timely intervention, extending windows for therapeutic efficacy—particularly important for neurodegenerative LSD forms where irreversible damage accumulates rapidly.
2. Evolving Therapeutic Arsenal
Enzyme replacement therapy remains a cornerstone for several LSDs, offering systemic disease control and proven clinical benefit in many patients. However, next-generation approaches are expanding options: small-molecule chaperones improve enzyme stability for amenable mutations; substrate reduction therapies lower pathogenic substrate buildup; and gene therapies strive for durable, one-time correction via viral vectors or ex vivo gene-modified cell transplantation. These modalities present significant upside if safety, durability, and delivery challenges can be met.
3. Gene Therapy Momentum
Multiple gene therapy programs—using AAV vectors or lentiviral ex vivo approaches—are advancing through clinical development for CNS and systemic LSD manifestations. Durable expression and reduced treatment frequency make gene therapy highly attractive commercially and clinically, especially for pediatric indications. Successful late-stage readouts and regulatory approvals could materially reshape long-term market economics.
4. Regulatory & Reimbursement Tailwinds
Orphan-drug incentives, accelerated pathways, and specialized reimbursement arrangements (outcomes-based contracts, annuity payments) have improved commercial viability for high-cost biologics and gene therapies. Payer willingness to fund transformative treatments—paired with patient advocacy pressure—continues to enable access despite premium pricing.
5. Growing Patient & Caregiver Advocacy
Patient organizations play a central role in raising awareness, funding natural history studies, supporting registries, and accelerating trial enrollment. Their engagement shortens development timelines and helps define meaningful clinical endpoints that matter to patients.
Market Challenges & Risk Factors
1. High Cost of Therapy & Affordability Issues
Long-term ERTs and one-time gene therapies carry substantial price tags. Ensuring sustainable access across public and private payers—while maintaining incentives for innovation—remains a complex policy and commercial challenge.
2. CNS Delivery & Unmet Neurological Needs
Many LSDs have significant central nervous system involvement. Delivering therapeutic payloads across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) safely and effectively is a major scientific hurdle; intrathecal, intraparenchymal, or engineered vector approaches increase complexity and cost.
3. Small, Heterogeneous Patient Populations
Rare disease trial design, statistical powering, and real-world evidence generation require creative regulatory strategies and global recruitment efforts. Heterogeneity in genotype–phenotype relationships complicates outcome interpretation and treatment personalization.
4. Immunogenicity & Long-Term Safety
Immune responses to replacement enzymes or viral vectors can limit efficacy or create safety concerns. Long-term follow-up for gene therapy recipients is essential to understand durability, insertional risks, and late adverse events.
Competitive Landscape & Strategic Implications
The market comprises established biopharma companies with approved ERTs, niche specialty developers focused on chaperones and SRTs, and an increasingly vibrant gene-therapy ecosystem of startups and academic spin-outs. Strategic partnerships—combining gene-therapy platforms, manufacturing scale, and clinical expertise—are common. Contract manufacturing capacity for viral vectors and cell therapies is a critical bottleneck; companies investing early in scalable, quality-assured production gain a competitive edge.
Commercial strategies that combine diagnostic outreach, newborn screening advocacy, flexible pricing models, and comprehensive patient support services (home infusion, adherence programs, genetic counselling) will optimize uptake. Real-world evidence programs and registries will be decisive for reimbursement negotiations and long-term market access.
Outlook (2025–2035)
Over the coming decade, the lysosomal storage disease treatment market is expected to broaden from a primarily ERT-driven field to a multi-modal landscape where gene therapies, targeted small molecules, and combination regimens meaningfully contribute. Successful clinical validation of durable gene therapies—particularly for CNS-involved LSDs—would represent a watershed, shifting economics from chronic lifetime therapy to potential one-time curative interventions. Meanwhile, incremental improvements in ERT formulations, delivery methods, and supportive care will continue to improve patient outcomes.
Companies that prioritize scientific rigor in CNS delivery, invest in manufacturing scale-up, collaborate with diagnostic networks, and engage proactively with payers and patient communities will be best positioned to lead this complex but high-impact therapeutic market. The decade ahead promises both profound clinical benefits for patients and new commercial models for rare-disease care.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/lysosomal-storage-disease-treatment-market