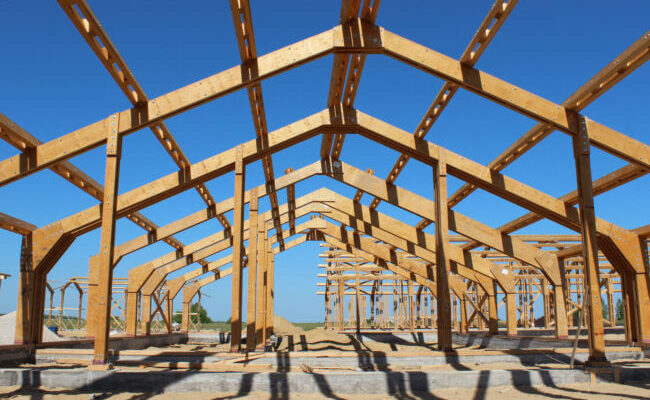
Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) is an engineered wood product made by bonding thin layers of wood veneers together with adhesive. It is known for its strength, durability, and versatility. LVL is commonly used in construction for applications such as beams, headers, joists, and columns.
The use of LVL in construction offers several advantages. Its uniform strength and resistance to warping or splitting make it a reliable choice for structural components. LVL also provides enhanced load-bearing capacity, allowing for longer spans and increased design flexibility. Additionally, LVL’s sustainable nature, as it is made from fast-growing plantation logs, contributes to its appeal in environmentally-conscious markets.
Unlocking the Potential of Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) in Modern Construction
In this edition, we shine the spotlight on Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) – an innovative engineered wood product that is revolutionizing the construction industry. Join us as we explore the various uses and discuss the future business prospects of this remarkable material.

Understanding Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL)
Delve into the composition and manufacturing process of LVL, gaining insights into how thin layers of wood veneers are bonded together to create a strong and durable building material. Learn about its unique properties, such as uniform strength, resistance to warping, and enhanced load-bearing capacity.
Versatility in Construction Applications
Discover the wide range of applications where LVL shines. From beams and headers to joists and columns, LVL offers exceptional performance as a structural component. Explore its design flexibility, spanning capabilities, and its ability to meet the demands of modern construction projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
In an era of heightened environmental consciousness, sustainability is a key consideration. Explore how LVL, made from fast-growing plantation logs, aligns with sustainable construction practices. Understand the environmental benefits it offers, including reduced carbon footprint and the preservation of natural resources.
Market Trends and Future Prospects
Stay ahead of the curve by exploring the current market trends and future business prospects of LVL. Gain insights into the growing demand for laminated veneer lumber, reliable and cost-effective construction materials, and how LVL’s performance characteristics position it as a preferred choice. Understand how the market’s focus on sustainability presents opportunities for manufacturers and suppliers.
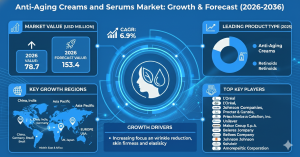
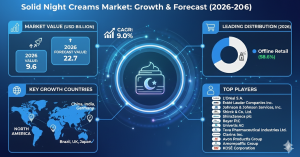
According to Fact.MR‘s analysis, the worldwide demand for laminated veneer lumber is projected to value worth US$ 6.11 billion by 2033.
Get complete Details
Benefits offered by Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL)

Strength and Durability
– Uniform strength: LVL’s manufacturing process ensures consistent strength throughout the entire product.
– Resistance to warping and splitting: LVL’s bonded layers provide stability, reducing the risk of warping or splitting over time.
– Enhanced load-bearing capacity: LVL’s engineered construction allows for greater load-bearing capabilities compared to traditional lumber.
Design Flexibility
– Longer spans: LVL’s strength allows for longer spans, reducing the need for additional support and enabling more open and spacious designs.
– Versatile sizes and shapes: LVL can be manufactured in various sizes and shapes, accommodating a wide range of architectural and design requirements.
– Compatibility with other building materials: LVL can be easily integrated with other materials, such as steel or concrete, to create hybrid structures.
Check this post about rising demand for Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL)
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
– Efficient use of resources: LVL is made from fast-growing plantation logs, reducing the demand for slow-growing hardwood species.
– Reduced carbon footprint: LVL production requires less energy compared to alternative materials, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions.
– Renewable and recyclable: LVL is a renewable resource, and at the end of its life cycle, it can be recycled or repurposed, minimizing waste.
Cost-effectiveness
– Material efficiency: LVL’s engineered construction maximizes the use of raw materials, minimizing waste and reducing costs.
– Labor savings: LVL’s uniformity and predictable performance simplify installation, leading to faster construction and potential labor cost savings.
– Long-term value: LVL’s strength and durability contribute to its longevity, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements and providing long-term cost savings.

Code Compliance and Safety
– Consistent performance: LVL’s engineered properties meet or exceed industry standards, ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations.
– Fire resistance: LVL has inherent fire-resistant properties, providing a higher level of safety compared to traditional lumber.
– Structural integrity: LVL’s strength and durability enhance the overall structural integrity of buildings, ensuring long-term safety for occupants.
Conclusion
We hope you have gained a deeper understanding of the immense potential of Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) in modern construction. Its strength, durability, versatility, and sustainability make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. Its unique properties make it an attractive choice for a wide range of construction applications, providing long-term value and contributing to sustainable building practices.
Stay tuned for more insightful articles as we continue to explore the fascinating world of construction materials.
Also Read: