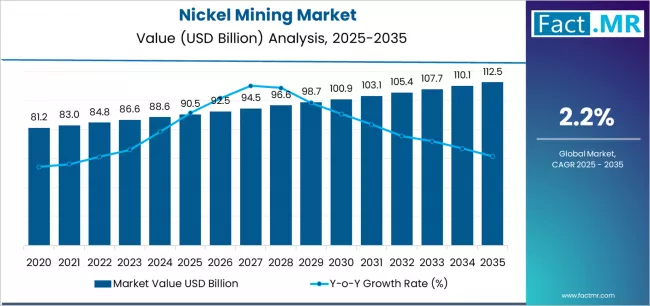
The global nickel mining market is entering a pivotal decade as demand dynamics shift from traditional stainless-steel end uses toward a rapidly growing appetite from battery manufacturers supporting electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage. Nickel’s role as a high-energy-density battery metal—especially in nickel-rich chemistries used for cathodes—combined with steady demand for stainless steel, means miners and refiners face both opportunity and pressure to scale sustainable, cost-efficient production while managing environmental and social expectations.
Quick Stats (qualitative snapshot)
-
Primary Demand Drivers: Stainless-steel production remains the largest historical consumer, while battery demand (EVs, grid storage) is the fastest-growing driver.
-
Key Supply Regions: Indonesia, the Philippines, Russia, Canada, Australia, Brazil, and New Caledonia—each with different ore types (laterite vs. sulphide) and processing pathways.
-
Major Market Themes: Securing low-cost, high-grade feedstock; expanding refining capacity for battery-grade nickel; improving ESG performance; and advancing nickel-sulfide exploration and project finance.
To access the complete data tables and in-depth insights, request a Discount On The Report here: https://www.factmr.com/connectus/sample?flag=S&rep_id=12235
Demand Dynamics
Historically, stainless steel has accounted for the lion’s share of nickel consumption, driven by construction, industrial machinery, and consumer goods. However, the electrification transition is materially altering demand composition. Nickel-rich lithium-ion battery chemistries—used especially in medium- and long-range EVs—require higher-purity nickel sulfide feedstock or upgraded laterite products processed through high-pressure acid leaching (HPAL) or mixed hydroxide precipitate (MHP) routes. As EV penetration rises worldwide and automakers scale production of nickel-rich cathodes, nickel demand from the battery sector is expected to be a dominant growth vector through 2035.
At the same time, demand for stainless steel remains resilient in emerging markets where urbanization and infrastructure projects continue. This dual demand profile gives nickel mining a balanced base while accelerating investment interest in projects that can supply battery-grade material.
Supply Considerations & Ore Types
Nickel occurs mainly in two ore systems: sulfide and laterite. Sulfide deposits produce nickel concentrate that is typically easier and cheaper to convert into refined, high-purity nickel suitable for battery cathodes. Laterite deposits—more abundant and widely distributed—often require more complex hydrometallurgical processing (e.g., HPAL) to yield battery-grade material. The recent surge in nickel consumption for batteries has prompted significant capital expenditure across the value chain: miners are re-ranking projects by metallurgy (sulfide vs. laterite), proximity to smelters/refineries, and ESG credentials.
Countries with large laterite resources have invested in downstream refining capacity to upgrade feedstock locally, while some firms pursue partnerships with smelters or invest directly in refining technologies. Security of supply, control of the refining step, and traceability are becoming central strategic priorities for OEMs and miners alike.
Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) Imperatives
Nickel mining faces intense scrutiny due to land-use impacts, energy intensity, water usage, and emissions associated with laterite processing. Battery makers and automakers are pushing for low-carbon, responsibly sourced nickel with transparent supply chains. This pressure has driven miners to invest in renewable energy for mining operations, more efficient processing technologies, better tailings and waste management, and community engagement programs to secure social license to operate. Projects that can demonstrate lower lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions and robust community benefits are likely to secure offtake agreements and premium partnerships with downstream users.
Technology & Processing Trends
To meet battery-grade specifications, the industry is adopting several processing pathways: expansion of HPAL plants for laterite upgrade, increased recycling of nickel from end-of-life batteries, development of mixed hydroxide precipitate (MHP) routes, and investments in cleaner electrowinning and smelting technologies. Battery-grade refinement capacity is becoming a bottleneck in some regions, prompting vertically integrated strategies where miners invest in refineries or enter long-term offtake and tolling agreements. In parallel, advances in extraction, automation, and digital mine operations are improving cost profiles and reducing environmental footprints.
Regional Outlook
Southeast Asia—particularly Indonesia and the Philippines—dominates mined nickel output, with Indonesia aggressively expanding downstream refining to capture more value domestically. Australia and Canada are important sources of higher-quality sulfide ore and are attractive for investors seeking projects with lower processing risk and stronger governance. Russia and Brazil provide significant reserves but can be subject to geopolitical and permitting considerations. New project development in Africa and Latin America is increasing as junior explorers target greenfield sulfide discoveries and laterite resources with favorable logistics.
Challenges & Risks
The nickel market faces several risks: volatility in nickel prices driven by cyclical stainless-steel demand and speculative trading; technical and commercial challenges in scaling HPAL plants; permitting delays and local opposition; and the capital intensity and long lead times of new mining and refining projects. Additionally, the pace of battery technology change—such as moves toward lower-nickel chemistries—could influence long-term demand scenarios, making flexible offtake arrangements and diversified end-market strategies prudent.
Strategic Implications & Outlook
Through 2035, the nickel market is expected to balance a stable base of stainless-steel demand with accelerating battery demand, leading to higher overall consumption and a re-rating of projects capable of delivering battery-grade nickel at competitive cost and low carbon intensity. Successful players will be those that secure high-quality, traceable feedstock; invest in downstream refining or strategic partnerships; demonstrate strong ESG performance; and maintain operational flexibility to serve both stainless-steel and battery markets. Recycling and secondary supply will become increasingly important, complementing primary production and helping meet quality and sustainability expectations.
In sum, nickel mining stands at the intersection of traditional industrial demand and a electrified future—rewarding capital discipline, technical excellence, and sustainability leadership with access to expanding, higher-value markets.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/nickel-mining-market