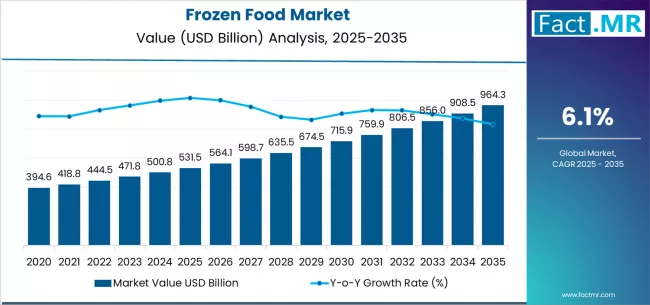
The global frozen food market continues to expand as changing consumer lifestyles, urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and demand for convenient, longer-shelf-life options drive consistent uptake. Frozen foods — spanning ready meals, vegetables, fruits, seafood, meat, bakery items, and desserts — offer food security, reduced waste, and year-round access to seasonal ingredients. Advances in freezing technology, cold-chain logistics, and consumer trust in quality have elevated frozen products from commodity staples to premium, value-added offerings across retail and foodservice channels.
Quick Stats (2025–2035)
-
Market Value 2025 (global, approx.): USD 280 billion
-
Forecast Market Value 2035 (global, approx.): USD 430 billion
-
Absolute Growth (2025–2035): ~USD 150 billion
-
Forecast CAGR (2025–2035): ~4.0%
-
Leading Category (2025): Frozen ready meals & prepared foods (~28% share)
-
Fastest-Growing Category: Premium frozen seafood & plant-based frozen items
To access the complete data tables and in-depth insights, request a Discount On The Report here: https://www.factmr.com/connectus/sample?flag=S&rep_id=12333
Key Market Drivers
1. Convenience & Time-Saved Eating
-
Consumers prioritize ready-to-heat and single-serve frozen meals due to busy lifestyles and multi-tasking routines.
-
Single-household living and remote working increase demand for convenient portioned frozen options.
2. Improved Freezing & Quality Retention Technologies
-
Shock freezing, cryogenic freezing, and IQF (individual quick freeze) maintain texture, flavor and nutrients.
-
Quality improvements increase consumer perception and willingness to pay for premium frozen offerings.
3. Year-Round Access to Seasonal & Specialty Items
-
Frozen categories enable year-round supply of seasonal fruits, vegetables, and seafood, stabilizing pricing and availability for retailers and manufacturers.
4. Reducing Food Waste & Extending Shelf Life
-
Frozen products lower spoilage across supply chains and promote sustainable inventory management for retailers and foodservice operators.
5. Rising Demand for Healthier & Specialty Options
-
Growth in organic frozen lines, clean-label ingredients, plant-based frozen meals, and low-sodium or low-sugar options responds to health-conscious consumers.
Market Structure & Segment Insights
By Product Category
-
Ready Meals & Prepared Foods: Largest segment; includes single-serve and family meals, ethnic cuisines, and premium chef-style offerings.
-
Frozen Vegetables & Fruits: High volume due to affordability and nutritional retention.
-
Frozen Seafood & Meat: Premiumization and traceability are driving growth in high-value species and sustainably sourced lines.
-
Bakery & Desserts: Growing impulse and convenience purchases (croissants, pastries, frozen cakes).
-
Plant-Based & Alternative Proteins: Rapidly expanding niche as vegan and flexitarian diets rise.
By Distribution Channel
-
Supermarkets & Hypermarkets: Primary sales channel for mainstream frozen products; focus on private-label and premium SKUs.
-
E-commerce & Online Grocery: Fastest-growing channel supported by cold-chain home delivery and click-and-collect services.
-
Foodservice & QSRs: Institutional demand for frozen intermediates and ready meals supports B2B volumes.
-
Convenience Stores & C-Stores: Growth in on-the-go frozen snacks and microwavable options.
By Region
-
North America & Europe: Mature markets with high per-capita frozen consumption and premiumization trends.
-
Asia-Pacific: Fastest growth driven by urbanization, rising incomes, and expanding modern retail and e-grocery.
-
Latin America & Africa: Emerging demand; opportunities tied to cold-chain investment and retail modernization.
Challenges & Restraints
-
Cold-Chain Infrastructure Gaps: In emerging markets, limited cold storage and transport capacity restrict market penetration.
-
Energy Costs & Sustainability Concerns: Freezing, storage and transport are energy-intensive; rising energy prices and emissions pressure require efficiency investments.
-
Consumer Perception & Freshness Bias: Some consumers still perceive fresh as superior — education and premium frozen positioning are needed.
-
Logistics & Last-Mile Delivery Complexity: Scaling e-grocery for frozen foods requires specialized packaging and reliable, low-temperature delivery solutions.
Opportunities & Strategic Directions
1. Premiumization & Product Innovation
-
Launch chef-style, ethnic, organic, and gourmet frozen lines to capture higher margins and differentiate from private-label commoditized SKUs.
2. Plant-Based & Functional Frozen Foods
-
Invest in plant-based ready meals, fortified frozen foods, and functional ingredients (protein-rich, fiber, probiotics) to meet health trends.
3. Cold-Chain Modernization & Localized Freezing Hubs
-
Build distributed freezing centers and micro-fulfillment sites close to urban demand centers to enable same-day frozen e-grocery delivery.
4. Sustainable Packaging & Energy Efficiency
-
Adopt recyclable, insulated packaging and invest in renewable energy for cold storage to reduce lifecycle emissions and meet sustainability commitments.
5. Enhanced Traceability & Transparency
-
Use QR codes and supply-chain storytelling for seafood and specialty products to increase trust and willingness to pay.
Outlook
The frozen food market is poised for durable growth to 2035, transitioning from a value-oriented staple category to one characterized by premium innovation, health functionality, and e-commerce penetration. Companies that combine superior freezing technologies, supply-chain resilience, product differentiation (including plant-based and premium seafood), and sustainable cold-chain practices will capture the largest share of the growing market. Demand will be strongest where modern retail, efficient logistics, and consumer convenience converge — making the frozen category a strategic growth area for food manufacturers and retailers alike.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/frozen-food-market