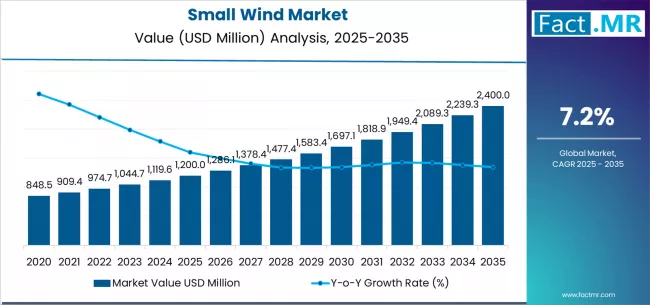
The transition toward sustainable energy solutions is reshaping the global power landscape, with small wind systems playing an increasingly vital role in decentralized energy generation. Designed to harness wind power at a local scale, these compact turbines are helping communities, businesses, and individuals reduce their dependence on conventional grids and fossil fuels.
As global decarbonization efforts accelerate, the small wind market is gaining traction due to its affordability, flexibility, and scalability. These systems are particularly suited for rural electrification, agricultural operations, small enterprises, and off-grid communities, where consistent and clean power is essential for development and resilience.
Market Overview
The small wind market encompasses turbines typically rated below 100 kW, engineered to generate electricity for individual homes, farms, and small commercial or industrial establishments. Unlike large wind farms that feed power directly into national grids, small wind systems are primarily distributed generation sources—installed at or near the point of energy consumption.
Their appeal lies in simplicity, adaptability, and environmental compatibility. With technological advancements improving turbine efficiency, material strength, and design aerodynamics, modern small wind systems are now capable of producing stable energy even at low wind speeds. Additionally, hybrid systems that integrate small wind turbines with solar photovoltaic (PV) setups are expanding energy reliability for users in remote or weather-variable regions.
Government initiatives promoting renewable adoption, combined with falling component costs and improved storage technologies, continue to expand the market’s potential. From microgrids to individual households, small wind solutions are now positioned as a critical enabler of the global clean energy transition.
Regional Insights
The adoption of small wind technology varies across regions, influenced by policy frameworks, geography, and energy infrastructure development:
- North America remains a leading market, supported by incentives for distributed renewable generation and strong consumer interest in energy independence. Rural communities, farms, and off-grid installations in the United States and Canada are key adopters.
- Europe follows closely, driven by ambitious renewable energy targets and supportive government subsidies. The United Kingdom, Germany, and Italy have seen increased installation of small wind systems, particularly in agricultural and coastal regions.
- Asia Pacific is emerging as a major growth hub due to rapid rural electrification programs and the expansion of hybrid renewable projects. Countries such as China and India are investing heavily in small wind to complement solar energy and reduce pressure on grid infrastructure.
- Latin America and Africa are also witnessing increasing interest, as small wind systems provide an affordable and scalable solution for communities without reliable grid connectivity.
Regional diversity in energy demand and policy support underscores the versatility of small wind technology in meeting localized power needs sustainably.
Key Trends & Forecast
Several notable trends are shaping the evolution of the small wind market:
- Hybrid Renewable Systems: Integration with solar PV, batteries, and smart inverters is enabling continuous power supply, even in fluctuating weather conditions. These hybrid setups are becoming a preferred choice for off-grid users and microgrid developers.
- Technological Advancements: Modern turbines feature lighter materials, improved blade designs, and advanced control systems that enhance efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. Innovations in vertical-axis turbines are also expanding deployment possibilities in urban and low-wind areas.
- Policy and Incentive Support: Governments worldwide are offering feed-in tariffs, net-metering schemes, and tax credits to encourage small wind adoption. These measures are accelerating installations, particularly in regions pursuing net-zero targets.
- Community Energy Projects: Small wind turbines are increasingly being deployed in cooperative and community-based energy programs, empowering local populations to generate and manage their own renewable power.
- Digitalization and Smart Monitoring: Integration of IoT-enabled sensors and remote monitoring software allows users to track performance, optimize generation, and schedule maintenance efficiently.
These advancements collectively highlight the industry’s shift toward smarter, more resilient, and user-driven renewable energy systems.
Applications & End-Use Outlook
The small wind market serves diverse applications across residential, commercial, industrial, and community sectors.
- Residential Use: Homeowners in remote or rural areas leverage small wind turbines for household energy needs, reducing electricity costs and reliance on traditional grids.
- Agricultural Sector: Farms utilize small wind systems to power irrigation, lighting, and equipment, ensuring stable energy access while lowering operational expenses.
- Commercial and Industrial Facilities: Small enterprises and workshops deploy turbines for self-generation, particularly where grid power is unreliable or expensive.
- Telecommunication and Infrastructure: Off-grid telecommunication towers and rural facilities use small wind systems for continuous, low-maintenance power supply.
- Community Electrification: In developing regions, small wind installations form part of microgrids that deliver clean energy to entire villages or clusters of homes.
By offering flexibility in installation and scalability in capacity, small wind systems have become an essential tool for distributed energy generation worldwide.
Competitive Landscape
The small wind market features a diverse mix of global and regional players focused on design innovation, cost reduction, and hybrid technology integration. Leading manufacturers are prioritizing aerodynamic optimization, lightweight composite materials, and digital control systems to improve performance across varying wind conditions.
Strategic collaborations between turbine producers, energy storage firms, and renewable developers are fostering the creation of holistic distributed energy ecosystems. Furthermore, local assembly and service networks are expanding, ensuring better accessibility and technical support in emerging markets.
The market’s competitive dynamics are also shaped by the growing rental and service-based model, which enables customers to adopt small wind solutions with lower upfront investment. With sustainability driving global policy and consumer behavior, companies offering efficient, quiet, and maintenance-friendly designs are expected to gain a distinct competitive advantage.
Conclusion
The small wind market stands at the intersection of innovation, sustainability, and decentralization. As global energy systems shift toward renewables, small wind turbines offer a practical and scalable path to clean power generation—especially in areas where grid infrastructure is limited or unreliable.
Future growth will be anchored in hybrid integration, smart controls, and local manufacturing capabilities that make small wind systems more accessible and cost-effective. For households, businesses, and communities seeking energy independence, small wind technologies represent a resilient and eco-friendly solution.
In an era where sustainability defines progress, the small wind market exemplifies how localized innovation can drive global energy transformation—delivering clean power, reducing carbon footprints, and empowering communities to take charge of their energy future.
Browse Full Report – https://www.factmr.com/report/small-wind-market