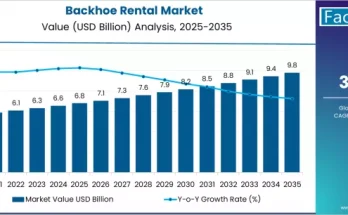
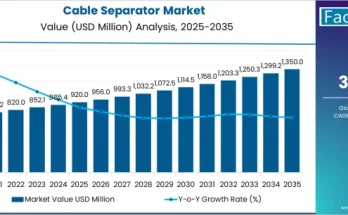
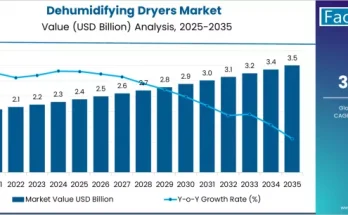
In modern power distribution systems, ensuring reliability, resilience, and fault management has become a top priority. One of the key technologies enabling this is the recloser control system — an intelligent solution that detects faults, isolates issues, and automatically restores power. As utilities worldwide continue to modernize their distribution networks, the recloser controls market is gaining momentum, driven by the global shift toward smart grids and digital transformation.
Recloser controls serve as the brain behind automatic circuit reclosers. They continuously monitor electrical conditions, detect faults, and determine when to open or close a circuit. With growing integration of renewable energy, distributed generation, and grid automation, these control systems have become essential to achieving efficient and reliable power distribution.
This article explores the structure, trends, and future of the recloser controls market — including major drivers, technological developments, regional insights, and competitive dynamics.
Market Overview
A recloser is an automatic high-voltage switch designed to interrupt power when faults occur and to automatically restore service after a brief pause if the fault is temporary. The recloser control unit governs this process. It decides how many times the recloser should open and close, the timing of each cycle, and how it communicates with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems.
Recloser controls today come in several forms, such as electronic, hydraulic, or hybrid systems. These devices not only perform fault detection and reclosing operations but also provide event recording, diagnostics, communication, and remote operation capabilities. As grid infrastructures become smarter and more decentralized, recloser controls are playing a crucial role in ensuring stable and intelligent power distribution.
Key Market Drivers
- Grid Modernization and Automation
The modernization of power grids is a primary growth driver for the recloser controls market. Many utilities are investing in automation systems to improve reliability, reduce downtime, and quickly identify fault locations. Smart recloser controls enable real-time fault detection, sectionalizing, and remote operation, making them indispensable in advanced distribution systems.
- Integration of Renewable Energy
The increasing penetration of renewable energy sources — such as solar and wind — has introduced new challenges to power stability. Recloser control systems equipped with adaptive protection settings help utilities manage fluctuating loads and bidirectional power flows, ensuring that renewable energy is efficiently integrated into the grid.
- Rising Demand for Reliability
Consumers expect uninterrupted power supply. Even short outages can disrupt industries, healthcare facilities, and urban infrastructure. By automatically isolating faults and restoring service, advanced recloser controls significantly enhance grid reliability and reduce outage duration, supporting utility performance targets.
- Technological Advancements
Microprocessor-based recloser controls with enhanced communication, data analytics, and predictive maintenance capabilities are transforming fault management. The evolution of digital sensors, communication modules, and embedded intelligence allows recloser controls to function as key nodes in smart distribution networks.
- Regulatory Support and Smart Grid Initiatives
Government programs promoting grid modernization and smart energy management are creating new opportunities for recloser control manufacturers. Regulations that encourage performance-based utility incentives also push companies to adopt automated systems that meet reliability and efficiency benchmarks.
Market Segmentation
The recloser controls market can be segmented based on several parameters:
By Type
- Electronic Controls: Utilize microprocessors and digital logic to provide precise, programmable reclosing operations. They dominate the market due to superior performance and compatibility with smart grid networks.
- Hydraulic Controls: Traditional mechanical systems still used in some rural or legacy installations due to their simplicity and durability.
- Hybrid Controls: Combine mechanical reliability with electronic intelligence, offering a balanced solution for transitional networks.
By Phase Type
- Single-Phase Reclosers: Used in rural and low-capacity networks.
- Three-Phase Reclosers: Common in high-capacity and industrial feeders.
- Triple Single-Phase Reclosers: Provide flexibility and improved fault isolation.
By Application
- Utilities: The largest segment, focused on distribution automation and fault management.
- Industrial and Commercial Users: Require reliable systems for uninterrupted operations.
- Renewable and Microgrid Projects: Increasing adoption to support decentralized energy management.
By End Use
Recloser controls find applications in both urban distribution systems and rural electrification projects, where reliability and low maintenance are essential.
Regional Insights
North America
North America leads the global market, supported by widespread adoption of smart grid technologies and ongoing investment in grid automation. The region’s utilities are upgrading aging infrastructure and implementing advanced recloser controls to comply with regulatory reliability standards and reduce outage durations caused by extreme weather events.
Europe
Europe’s market growth is influenced by stringent energy regulations and high renewable energy integration. Countries are investing in digital control systems that support distributed generation and meet environmental goals. Focus areas include improving power quality, grid flexibility, and interoperability between control devices and renewable systems.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region for recloser controls. Rapid industrialization, rising electricity demand, and government initiatives to modernize aging distribution infrastructure are fueling growth. Developing economies such as China and India are heavily investing in smart grids and rural electrification, where recloser controls play a vital role in maintaining network stability.
Latin America, Middle East, and Africa
These emerging markets are gradually adopting recloser controls to enhance grid resilience and reduce operational losses. Urbanization and new electrification programs are driving deployments, although adoption rates vary due to cost constraints and uneven infrastructure development.
Competitive Landscape
The recloser controls market is moderately consolidated, featuring both established multinational companies and regional players. Leading manufacturers are focusing on technology upgrades, advanced communication features, and long-term service partnerships with utilities.
Key players include companies specializing in electrical equipment, automation systems, and protection solutions. Their strategies often revolve around:
- Technological innovation: Development of recloser control units with improved sensors, data analytics, and remote communication capabilities.
- Integration with smart grid platforms: Ensuring compatibility with SCADA, DMS, and IoT frameworks.
- Product customization: Offering tailored control systems for different voltage classes, environmental conditions, and network configurations.
- After-sales service and training: Providing continuous support, monitoring, and software updates to enhance performance and reliability.
The competition is driven by efficiency, product reliability, local technical support, and the ability to deliver modular upgrades to existing recloser systems.
Challenges and Restraints
Despite positive market trends, the recloser controls industry faces several challenges:
High Installation and Integration Costs
Initial deployment costs can be substantial, particularly for utilities managing large, dispersed networks. Budget limitations often delay modernization efforts, especially in developing regions.
Interoperability and Compatibility Issues
Utilities operate a mix of legacy and modern equipment. Integrating new recloser controls into existing systems requires technical coordination, compatibility with communication protocols, and comprehensive testing.
Skill and Training Gaps
Operating and maintaining advanced recloser control systems require skilled personnel. In regions lacking technical expertise, inadequate training can lead to inefficient system utilization.
Cybersecurity Concerns
As recloser controls become more connected through IoT and wireless communication, ensuring data protection and system security is essential to prevent unauthorized access or operational disruptions.
Environmental and Operational Challenges
Recloser controls must withstand harsh environmental conditions such as high temperatures, humidity, and dust. Designing robust systems that maintain performance under such circumstances remains a key engineering focus.
Emerging Trends
The recloser controls market is undergoing a technological transformation. Several trends are shaping its future direction:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being embedded into control systems to predict faults, analyze performance data, and optimize reclosing sequences. This shift toward self-learning systems enhances operational efficiency and grid reliability.
- Edge Computing and Decentralized Control
Modern recloser controls are evolving toward edge intelligence, enabling faster, localized decision-making without dependence on centralized systems. This decentralization improves fault response time and reduces communication delays.
- IoT Connectivity and 5G Integration
The use of advanced communication networks allows utilities to collect and analyze data in real time. IoT-enabled recloser controls provide continuous monitoring and seamless integration with smart grid management platforms.
- Modular and Retrofit Solutions
Manufacturers are developing modular recloser control units that can be easily retrofitted to existing installations. This reduces costs, simplifies upgrades, and extends the lifespan of older infrastructure.
- Microgrid and Renewable Integration
Recloser controls are increasingly used in microgrid environments, where they manage transitions between grid-connected and islanded operations. This ensures stable power flow and efficient renewable energy management.
Future Outlook
The future of the recloser controls market is aligned with the evolution of intelligent power distribution. Utilities worldwide are expected to increase their investment in automation technologies that support predictive maintenance, improve operational transparency, and reduce system losses.
Advancements in sensors, communication technologies, and analytics will enable recloser controls to become more adaptive and data-driven. Over the next decade, greater emphasis will be placed on interoperability, cybersecurity, and modular scalability.
As electrification expands in developing regions and renewable energy integration accelerates, the demand for advanced recloser controls will continue to rise. The technology will remain a cornerstone of the modern power grid, bridging the gap between reliability, sustainability, and digital intelligence.
Conclusion
Recloser controls are transforming how utilities manage power distribution, delivering enhanced fault detection, faster restoration, and smarter grid coordination. As the energy landscape evolves toward cleaner and more decentralized systems, recloser controls provide the reliability backbone that supports this transition.
With growing investments in automation, rising renewable integration, and rapid advancements in control technologies, the recloser controls market is poised for steady growth in the coming decade.
Utilities, industrial operators, and technology providers that embrace innovation in recloser control solutions will be well positioned to lead the charge toward a more resilient and intelligent power future.