The regenerative medicines market is a rapidly evolving sector with significant potential for growth. It covers a range of cutting-edge technologies and therapies aimed at repairing, replacing, or regenerating damaged tissues or organs within the human body. These therapies held promise for treating a wide array of medical conditions, from orthopedic injuries to chronic diseases.
Regenerative medicine is a cutting-edge field of medical science that focuses on harnessing the body’s natural healing processes to repair, replace, or regenerate damaged or diseased tissues and organs. It holds great promise for treating a wide range of medical conditions and has the potential to revolutionize healthcare in the coming years. Regenerative medicine is founded on the principles of stimulating the body’s innate ability to heal itself. It aims to restore normal structure and function to damaged tissues or organs rather than merely managing symptoms.
Will the Regenerative Medicine Market pace well in North America?
In North America, the region is experiencing high growth due to various factors such as increasing investments in research and development, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and a growing aging population.
A few important trends in the market are:
- Emphasis on Stem Cell Therapies: Stem cell therapies were a major focus in regenerative medicine. They held immense potential for treating various conditions such as heart diseases, neurological disorders, and orthopedic injuries. The market was witnessing advancements in the utilization of pluripotent and induced pluripotent stem cells, with ongoing clinical trials and regulatory approvals.
- Growing Importance of Tissue Engineering: Tissue engineering was a crucial aspect of regenerative medicine, involving the creation of functional biological tissues in the lab for transplantation. This field was advancing rapidly, with innovations in 3D bioprinting, biomaterials, and organ transplantation techniques.
- Regulatory Environment: The regulatory framework for regenerative medicine products was evolving. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) were actively working to establish clear guidelines for the approval and commercialization of these therapies. This played a significant role in shaping the market landscape.
- Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships: Academic institutions, research organizations, and pharmaceutical companies were increasingly forming collaborations to accelerate research and development efforts in regenerative medicine. These partnerships facilitated the pooling of expertise, resources, and knowledge.
- Patient Awareness and Acceptance: Awareness among patients about regenerative medicine treatments was growing. Patients were becoming more receptive to these innovative therapies, seeking alternative and potentially more effective treatment options, especially for conditions with limited or no conventional treatment options.
- Economic Impact: The regenerative medicines market had the potential to significantly impact the healthcare economy in North America. Successful development and commercialization of these therapies could lead to reduced healthcare costs in the long run, especially for chronic diseases that currently incur high treatment expenses.
Emergence of Gene Therapies:
Gene therapies were gaining prominence as a key component of regenerative medicine. These therapies involved modifying or replacing faulty genes with healthy ones to address genetic disorders. The North American market was seeing significant investments and research efforts in this area, with several promising treatments making their way through clinical trials.
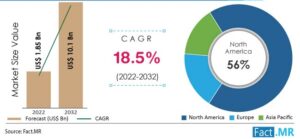 The gene therapy market size is projected to grow from US$ 1.85 Billion in 2022 to US$ 10.1 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 18.5% during the forecast period. A surge in rare disease cases worldwide is driving demand for cell and gene therapy, with ex-vivo gene therapy gaining popularity in neurological treatments. This trend is anticipated to propel the gene therapy market growth through 2032.
The gene therapy market size is projected to grow from US$ 1.85 Billion in 2022 to US$ 10.1 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 18.5% during the forecast period. A surge in rare disease cases worldwide is driving demand for cell and gene therapy, with ex-vivo gene therapy gaining popularity in neurological treatments. This trend is anticipated to propel the gene therapy market growth through 2032.
Key initiatives that have been adopted in the Asia Pacific market:
The Asia-Pacific region, with its large and aging population, has presented substantial growth potential for the regenerative medicine market. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and age-related conditions has created a significant demand for innovative treatment options.
- India has established guidelines for stem cell research and therapy to ensure ethical and safe practices. These guidelines are overseen by agencies like the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). The SCRRM program was initiated to promote stem cell research and regenerative medicine in India. It provided grants for research projects and collaborations. Moreover, The DBT in India has been instrumental in promoting research and development in biotechnology, including regenerative medicine. They provide funding and support for projects in this field.
- China’s government outlined a strategic plan to support and develop the regenerative medicine industry in its 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-2020). This included investment in research, development, and clinical applications. NSRRC in China serves as a centralized resource for stem cell and regenerative medicine research. It provides a platform for sharing resources and expertise.
- Moreover, Japan passed the Regenerative Medicine Promotion Act in 2013, which aimed to expedite the approval process for regenerative medicine products. This act established a regulatory framework for the industry. Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED): AMED is a Japanese government agency dedicated to promoting medical research and development. They support various initiatives related to regenerative medicine. Besides this, Japan has been actively conducting clinical trials for regenerative medicine products. Notably, the first-ever approved induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-based clinical trial for treating macular degeneration took place in Japan.
Various challenges in the regenerative medicine market:
- Demonstrating the safety and efficacy of regenerative therapies through rigorous clinical trials is essential. Many therapies are still in the experimental stage, and their long-term outcomes and potential side effects need thorough evaluation. Moreover, Developing and commercializing regenerative therapies often involves navigating complex regulatory processes. Regulators must balance the need for innovation with patient safety, which can lead to delays and uncertainty in market entry.
- Research and development costs for regenerative therapies can be exceptionally high due to the need for specialized equipment, skilled personnel, and extensive preclinical and clinical testing. This cost can limit the number of companies that can enter the market.
- Producing consistent and high-quality regenerative products can be challenging. Maintaining the purity and potency of cell-based therapies, for example, can be complex and costly.
Key companies in the market:
- Novartis: Novartis is a pharmaceutical company actively involved in regenerative medicine research and development, particularly in the field of cell and gene therapies. They have commercialized CAR-T cell therapies for certain types of cancer.
- Gilead Sciences: Gilead Sciences has a subsidiary called Kite Pharma, which is known for its CAR-T cell therapies, including Yescarta for the treatment of certain lymphomas.
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals: Regeneron is engaged in regenerative medicine research, with a focus on developing monoclonal antibodies and other biologic therapies for various diseases, including eye conditions and cancer.
- Bluebird Bio: Bluebird Bio specializes in gene and cell therapies, including those for rare genetic disorders and blood disorders like sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia
- Athersys: Athersys is known for its MultiStem cell therapy platform, which is being studied for various applications, including stroke, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Fate Therapeutics: Fate Therapeutics focuses on developing off-the-shelf cellular immunotherapies using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) for cancer treatment.