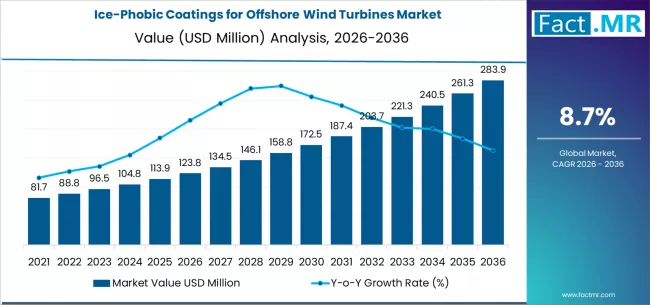
The ice-phobic coatings market for offshore wind turbines is evolving from a niche protective solution into a strategic enabler of cold-climate offshore wind expansion. As offshore wind capacity accelerates across Northern Europe, East Asia, and North America, the ability to mitigate icing-related downtime, blade damage, and safety risks is becoming central to asset performance and lifecycle economics.
Market Size and Growth Trajectory to 2036
By 2036, the global ice-phobic coatings for offshore wind turbines market is projected to reach approximately USD 284–545 million, growing from an estimated USD 124–229 million in 2026 at a CAGR of 8.7–9% over the decade. This growth outpaces many traditional industrial coating segments and reflects the structural expansion of offshore wind in icing-prone regions.
The broader wind power coatings market is forecast to grow from USD 1.7 billion in 2025 to nearly USD 4.9 billion by 2035, at an 11% CAGR, with offshore installations accounting for more than half of total demand. Ice-phobic solutions represent one of the fastest-growing sub-segments within this market, supported by their direct impact on energy yield and maintenance cost reduction.
Portfolio Priorities: From Anti-Icing to Performance Optimization
Historically, ice mitigation relied on active systems such as blade heating and mechanical de-icing. By contrast, next-generation ice-phobic coatings emphasize passive ice shedding, durability in saline environments, and compatibility with erosion-resistant topcoats. Polymer-based ice-phobic coatings already account for roughly 30% of coating-type share due to their balance of hydrophobicity, adhesion, and cost efficiency.
Strategic portfolios are increasingly prioritizing:
-
Hybrid coatings combining ice-phobic and anti-erosion properties to reduce leading-edge wear.
-
Longer recoat cycles, aligning with offshore maintenance intervals of 5–7 years.
-
Environmentally compliant formulations, as regulations tighten controls on fluorinated chemistries.
For coating suppliers, differentiation is shifting from basic ice resistance toward measurable gains in turbine availability and annual energy production (AEP), metrics closely tracked by offshore wind operators.
Adoption Trends Across Key Regions
Adoption is strongest in Northern Europe, where offshore wind farms face persistent low temperatures, sea spray, and icing events that can reduce power output by double-digit percentages during winter months. The United States and Canada are emerging as high-growth markets, with offshore wind forming a core pillar of long-term clean energy strategies in cold coastal zones.
In Asia, China and Japan are investing in offshore wind projects in northern and typhoon-exposed waters, accelerating demand for advanced protective coatings. India, while still in the early stages of offshore wind deployment, is projected to see double-digit CAGR (around 12%) in ice-phobic coating demand as pilot projects move toward commercialization.
Browse Full Report : https://www.factmr.com/report/ice-phobic-coatings-for-offshore-wind-turbines-market
Future Demand Outlook to 2036
Looking ahead, demand for ice-phobic coatings will be shaped by three structural drivers. First, the offshore wind turbine market itself is forecast to grow from USD 16.6 billion in 2025 to over USD 61.7 billion by 2035, creating a larger installed base requiring specialized surface protection. Second, climate variability is increasing the frequency of freeze–thaw cycles, amplifying icing risks even in regions previously considered marginal. Third, operators are prioritizing total cost of ownership, favoring passive solutions that reduce reliance on energy-intensive active de-icing systems.
By 2036, ice-phobic coatings are expected to evolve from optional add-ons to standard specifications for offshore turbines deployed above certain latitudes, particularly for blade applications, which already represent about 45% of total demand. For investors and suppliers, the market offers a compelling combination of recurring maintenance demand, technology differentiation, and alignment with global decarbonization goals.
In summary, the ice-phobic coatings for offshore wind turbines market is on a clear growth path toward 2036, underpinned by robust offshore wind expansion, advancing materials science, and a strategic shift toward performance-driven asset protection.