The global transition toward low-carbon, circular chemical value chains is positioning next-generation bio-based acetic acid as a strategic growth market over the 2026–2036 period. Driven by advances in industrial biotechnology, tightening environmental regulations, and rising demand from food, pharmaceutical, textile, and polymer industries, bio-based acetic acid is moving from niche adoption to mainstream commercialization.
Market Size and Revenue Outlook (2026–2036)
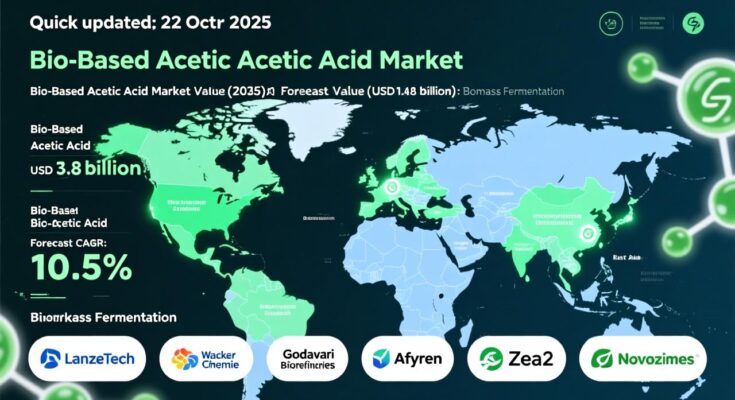
The global bio-based acetic acid market was valued at approximately USD 1.4 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 3.8 billion by 2035, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 10.5% over the decade. This growth rate significantly outpaces that of conventional petrochemical acetic acid, highlighting accelerating substitution dynamics.
Regionally, North America and Europe are expected to account for over 55% of incremental revenue growth between 2026 and 2036, supported by strong policy incentives and mature bio-manufacturing infrastructure. The United States bio-based acetic acid market alone is forecast to grow from about USD 0.4 billion in 2025 to USD 1.2 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 10.8%, generating more than USD 725 million in absolute new value.
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and India, is anticipated to be the fastest-expanding region post-2030, fueled by large-scale fermentation capacity investments and rising demand from textile processing, food preservatives, and vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) production.
Innovation Catalysts Reshaping the Market
Innovation is the central force underpinning next-generation bio-based acetic acid growth. Biomass fermentation technologies currently dominate with over 60% market share, benefiting from improved microbial strains, higher yields, and reduced downstream purification costs. The emergence of waste-to-chemicals platforms, utilizing agricultural residues, municipal organic waste, and industrial off-gases, is further lowering feedstock risk and enhancing sustainability metrics.
Key innovation catalysts include:
-
Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering, enabling higher acetic acid titers and productivity from non-food feedstocks.
-
Carbon capture and utilization (CCU) pathways, where captured CO₂ or industrial emissions are converted into acetic acid via gas fermentation.
-
Hybrid enzymatic–chemical processes, reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared with traditional petrochemical routes.
Between 2030 and 2035, more than 60% of total market expansion is expected to occur, coinciding with commercialization of advanced fermentation plants and scale-up of circular economy technologies.
Regulatory Impact and Policy Tailwinds
Regulatory frameworks are playing a decisive role in accelerating adoption. The European Union’s Green Deal, expanded carbon pricing mechanisms, and stricter REACH compliance requirements are increasing the cost of fossil-based acetic acid production, improving the relative economics of bio-based alternatives. In parallel, U.S. federal and state-level incentives—including tax credits for bio-manufacturing and grants under clean industrial policies—are reducing capital risk for new projects.
Globally, sustainability-linked procurement standards among multinational consumer goods and chemical companies are driving long-term offtake agreements for bio-based acetic acid. These contracts are providing revenue visibility and enabling producers to secure financing for next-generation facilities.
Application Trends and Demand Shifts
From an application standpoint, food and beverage uses account for approximately 42% of global demand, driven by consumer preference for naturally derived preservatives and acidity regulators. Pharmaceutical intermediates and sustainable packaging are expected to be the fastest-growing application segments between 2026 and 2036, supported by regulatory pressure to reduce solvent toxicity and lifecycle emissions.
In the chemical sector, bio-based acetic acid is increasingly being used as a feedstock for vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), adhesives, coatings, and biodegradable polymers. As brand owners commit to Scope 3 emission reductions, demand for low-carbon intermediates is forecast to rise sharply post-2028.
Browse Full Report : https://www.factmr.com/report/1189/bio-based-acetic-acid-market
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Outlook
The market remains moderately consolidated, with leading innovators including LanzaTech, Wacker Chemie, Godavari Biorefineries, Afyren, Zea2, and Novozymes, all investing heavily in scale-up and process optimization. Strategic collaborations between technology providers, agricultural producers, and chemical majors are expected to intensify through 2036.
Looking ahead, the next decade will be defined by cost convergence with petrochemical acetic acid, broader regulatory harmonization, and integration of bio-based acetic acid into global chemical supply chains. By 2036, bio-based routes are projected to represent a materially larger share of total acetic acid production, reinforcing their role as a cornerstone of the sustainable chemicals economy.
About the Market Outlook
This press release highlights key trends shaping the Next-Generation Bio-Based Acetic Acid Market (2026–2036), including innovation catalysts, regulatory dynamics, and revenue forecasts, based on aggregated industry intelligence and forward-looking analysis.