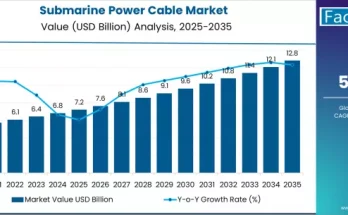
Submarine technology has evolved dramatically over the past century, transitioning from human-powered vessels to sophisticated underwater platforms capable of executing complex defense operations. Central to this evolution is the Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) system, a technology that enables submarines to operate submerged for extended periods without surfacing for air. The global submarine AIP system market is experiencing steady growth, reflecting the rising need for stealth, endurance, and operational efficiency in modern naval fleets. The increasing adoption of AIP systems underscores the strategic importance of these technologies in maintaining maritime security and enhancing submarine performance.
Market Overview:
The submarine AIP system market includes various technologies designed to provide diesel-electric and hybrid submarines with extended underwater endurance. Key types include fuel cells, Stirling engines, and closed-cycle diesel AIP systems. These systems complement traditional propulsion methods, allowing submarines to remain submerged longer, reduce noise and thermal signatures, and operate more efficiently. By minimizing the need to surface or use snorkels, AIP-equipped submarines enhance stealth, making them crucial assets in modern naval operations.
Submarine AIP systems are adopted not only for military superiority but also for strategic cost-efficiency. Unlike nuclear-powered submarines, AIP-equipped conventional vessels are less expensive to build and maintain, while offering significant operational advantages in terms of endurance and tactical versatility. The market is driven by technological innovations that improve energy efficiency, operational reliability, and automation of control systems.
Regional Insights:
North America, particularly the United States, remains a key market for submarine AIP systems, driven by ongoing initiatives to enhance the endurance and stealth capabilities of naval fleets. The U.S. Navy prioritizes technologies that allow submarines to conduct clandestine surveillance and defensive operations while minimizing detection risk.
Europe is also witnessing growth, with countries investing in modernized fleets and AIP-enabled submarines to maintain strategic maritime influence. Meanwhile, East Asia represents a significant share of the global market, reflecting increasing defense budgets and modernization programs in countries such as Japan and South Korea. These regions are integrating advanced AIP technologies to bolster operational readiness and technological advantage in underwater warfare.
Key Trends & Forecast:
- Extended Underwater Endurance:
The primary driver of AIP adoption is the need for prolonged submerged operations. Second-generation AIP systems significantly enhance endurance, allowing submarines to remain underwater longer than traditional diesel-electric counterparts. This capability reduces the risk of detection, enabling more effective surveillance and combat missions. - Technological Advancements in Propulsion:
Innovation in closed-cycle diesel, fuel cell, and Stirling engine technologies is enhancing efficiency and reliability. Developments such as energy-efficient vacuum pumps, variable speed drives, and intelligent control systems optimize submarine performance while reducing operational costs. - Shift Towards Cost-Efficient Submarines:
Conventional AIP-equipped submarines offer a more affordable alternative to nuclear-powered vessels without compromising operational capabilities. This cost advantage encourages navies to expand their fleets with technologically advanced yet budget-conscious submarines. - Increased Defense Spending:
Rising global defense budgets support research, development, and procurement of AIP-equipped submarines. Governments are investing in modernizing fleets to improve maritime security and strategic presence, further driving market demand. - Focus on Stealth Operations:
AIP systems reduce acoustic and thermal signatures, enhancing submarine stealth. This is critical for clandestine operations, surveillance, and deterrence missions. Navies are prioritizing AIP integration to maintain strategic advantage in high-risk maritime regions.
Applications & End-Use Outlook:
Submarine AIP systems are primarily utilized in military applications to enhance fleet capabilities. Conventional diesel-electric submarines benefit from reduced surfacing requirements, which decreases vulnerability to detection. The systems are also employed in hybrid and nuclear-powered submarines to optimize energy management and operational flexibility. Modern navies leverage AIP-equipped submarines for coastal defense, strategic deterrence, intelligence gathering, and special operations.
Market Dynamics:
- Drivers of Growth:
- Rising Demand for Operational Flexibility:Extended submerged operations enable strategic advantages, motivating navies to adopt advanced AIP technologies.
- Defense Modernization Programs:Investments in upgrading fleets with AIP systems are a major factor supporting market expansion.
- Technological Innovation:Continuous improvements in propulsion, energy efficiency, and automation are fueling adoption.
- Cost Advantages Over Nuclear Submarines:AIP-equipped conventional submarines provide a more affordable yet capable alternative.
- Challenges for Manufacturers:
- Technical Complexity:AIP systems require advanced engineering and manufacturing expertise to operate reliably under extreme underwater conditions.
- Safety Concerns:Handling fuels and materials used in AIP systems demands rigorous safety measures, complicating maintenance and operation.
- High R&D Costs:Developing next-generation AIP technologies involves substantial investment, which may be a barrier for some manufacturers.
Country-Specific Insights:
- United States:The U.S. Navy is enhancing submarine stealth and endurance to improve mission effectiveness. Extended underwater capabilities support clandestine operations and surveillance, making AIP systems essential for strategic advantage.
- Japan:Japan is modernizing its submarine fleet to enhance operational effectiveness and maintain technological superiority in defense. AIP integration allows longer submerged operations, improving combat readiness and naval stealth.
- East Asia:Countries in East Asia are increasingly investing in AIP-equipped submarines to strengthen maritime defense capabilities. This region is expected to maintain a significant market share due to ongoing fleet modernization and security concerns.
Category-wise Insights:
The market segments include line fit and retrofit options. The line fit segment dominates due to high demand for modernized AIP systems in newly built submarines. Closed-cycle diesel systems are particularly favored for their silent operation, increased endurance, and suitability for contemporary naval strategies. Diesel-electric submarines continue to be the primary end-users of AIP technology due to operational cost-efficiency and stealth advantages.
Competitive Landscape:
Key market players focus on technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and product diversification. Leading companies include Siemens, Navantia, General Dynamics, United Shipbuilding Corporation, CSICL, Kongsberg Gruppen, Lockheed Martin Corporation, SAAB, ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems, China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation, United Technologies Corporation, and DCNS. These companies are investing in next-generation AIP technologies, aiming to enhance submarine performance, operational reliability, and stealth capabilities.
Future Outlook:
The submarine AIP system market is poised for moderate yet consistent growth. Short-term trends (2024–2027) suggest an increase in AIP adoption for conventional submarines and new fleet constructions. Medium-term developments (2027–2030) focus on second-generation systems that enhance endurance, reduce acoustic signatures, and optimize energy management. Long-term projections (2030–2034) anticipate significant improvements in automation, propulsion efficiency, and system reliability, ensuring continued market expansion and operational excellence.
Navies worldwide are expected to increasingly prioritize stealth, endurance, and cost-efficiency when procuring AIP-equipped submarines. Manufacturers investing in advanced technologies, safety protocols, and strategic partnerships will capture market share and strengthen their position in this highly specialized industry.
Conclusion:
The submarine AIP system market represents a vital component of modern naval operations. By enabling extended submerged periods, reducing acoustic and thermal signatures, and providing cost-effective alternatives to nuclear-powered vessels, AIP technologies enhance fleet capabilities and operational effectiveness. Continuous innovation, strategic investments, and global defense modernization initiatives are shaping the market’s future. As countries strive to strengthen maritime security and maintain strategic advantage, submarine AIP systems will remain a critical asset in naval defense, driving growth and technological advancements well into the future.