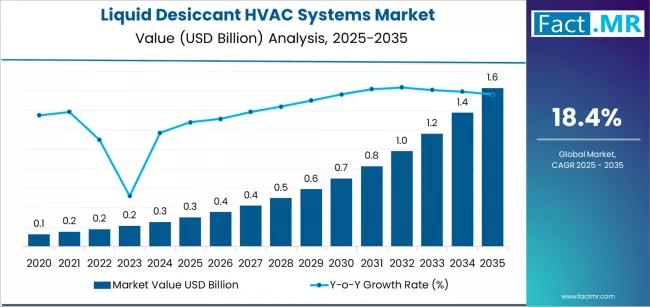
As the world intensifies its focus on sustainable building infrastructure and energy efficiency, the liquid desiccant HVAC systems market is emerging as a powerful force in modern climate control. These systems offer a compelling alternative to traditional vapor-compression cooling by integrating advanced dehumidification with energy-efficient regeneration mechanisms. They are rapidly gaining traction in commercial, industrial, and institutional settings, driven by the increasing demand for better humidity control and lower energy consumption.
Understanding Liquid Desiccant HVAC Systems
Liquid desiccant HVAC systems use a hygroscopic (moisture-absorbing) liquid—often a salt solution—to remove humidity from air. This moisture-laden desiccant is then regenerated by applying heat, allowing the system to recycle the desiccant and sustain continuous dehumidification. Because the system separates humidity control from temperature control, it can optimize both independently—leading to improved indoor air quality and energy savings.
These systems can be implemented in different configurations, including heat pump AC systems, dehumidifiers, and chiller-integrated designs, depending on the application and climate needs.
What Is Driving Market Growth?
Several macro trends are fueling the adoption of liquid desiccant HVAC systems. First, there is growing pressure on building operators to reduce energy costs while maintaining indoor comfort. As energy prices rise and sustainability goals become more central, systems capable of dehumidifying air efficiently without excessive electricity use have become attractive. Liquid desiccant systems achieve this by using low-grade heat for regeneration—often sourced from waste heat, solar thermal, or other renewable sources.
Second, demand for high-quality indoor air—especially in climate-sensitive environments like data centers, hospitals, and industrial plants—is increasing. These applications require very precise humidity control to ensure reliable operations and protect sensitive equipment or products. Liquid desiccant systems deliver strong moisture removal without excessive overcooling, making them ideal for such scenarios.
Third, the push for green buildings is supporting adoption. Certifications like LEED and BREEAM encourage energy-efficient, low-carbon designs, and liquid desiccant HVAC naturally aligns with those principles. Facility managers and developers are increasingly turning to these systems to meet sustainability targets and reduce their carbon footprint.
Key Segments in the Market
To understand how the liquid desiccant HVAC market is structured, it helps to look at its major segments:
- By Equipment Type
- Liquid Desiccant Heat Pump AC Systems: These are the most dominant, combining dehumidification and cooling in one integrated unit. Their ability to deliver both cooling and moisture control makes them especially attractive for commercial and industrial use.
- Liquid Desiccant Dehumidifiers: Designed for applications where only humidity control is needed—such as clean rooms, food processing, or pharmaceuticals.
- Liquid Desiccant Chiller-Integrated Systems: These systems integrate desiccant technology with traditional chiller infrastructure, enabling large-scale or district cooling scenarios.
- By Application
- Commercial: The largest segment, including office buildings, data centers, retail, and hospitality. These buildings have intensive cooling loads and require tight humidity control.
- Industrial: Includes manufacturing, pharmaceutical, food processing, and other sectors where precise environmental control is critical.
- Residential: Although a smaller part of the market currently, there is potential for high-end residential systems or green homes to adopt liquid desiccant solutions as technology matures and costs decline.
- By Region
- Asia Pacific is expected to be a major growth driver, thanks to rapid urbanization, booming commercial real estate, and increasing emphasis on energy-efficient cooling.
- North America has strong adoption due to mature commercial infrastructure, data center growth, and regulatory frameworks encouraging efficiency.
- Europe is also a key region, driven by stringent building energy codes and commitments to sustainability.
Opportunities & Challenges
Opportunities:
- The growing construction of data centers worldwide offers a significant opportunity. These facilities not only demand efficient cooling but also very tight humidity control, making liquid desiccant systems a strategic fit.
- Green building retrofits and net-zero building projects provide fertile ground for adopting desiccant HVAC systems. As older buildings renovate, there is an opportunity to improve their energy profiles with more efficient dehumidification.
- Advances in IoT, building automation, and control systems are enabling smarter liquid desiccant deployment. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and integration with building energy management systems can significantly improve performance and reduce operational costs.
Challenges:
- High upfront costs remain one of the biggest barriers. The specialized equipment, heat regenerators, and control systems make initial investments steeper than traditional HVAC systems.
- Technical complexity is another issue: designing, installing, and commissioning liquid desiccant systems requires expertise that may not be widely available among HVAC contractors.
- Integration with existing HVAC infrastructure can be tricky. In retrofit projects, ensuring compatibility with chiller plants, ductwork, and building automation systems demands careful planning.
- Regeneration energy requirement: While these systems can use low-grade heat, securing a consistent and cheap regeneration heat source is crucial for maximizing savings. Without that, the economic case weakens.
Emerging Trends to Watch
- Smart Regeneration: Systems are increasingly being designed to smartly manage regeneration cycles based on demand, external temperature, and available heat sources, improving efficiency.
- Renewable Integration: Liquid desiccant systems dovetail well with renewable thermal energy sources. Solar thermal, waste heat from industrial processes, or geothermal sources can help regenerate desiccant → lowering operational costs.
- Modular and Scalable Designs: Manufacturers are developing modular desiccant units that can be scaled up or down based on building size and load — this flexibility helps lower installation risk and capital cost.
- Increasing Collaborations: HVAC companies, building automation firms, and desiccant solution providers are collaborating more closely. These partnerships help reduce implementation risk and enable end-to-end solutions.
Key Players & Competitive Landscape
Several companies are pioneering in the liquid desiccant HVAC field. Notable names include firms that specialize in energy-efficient HVAC technologies, as well as those building proprietary desiccant loops, heat exchangers, and control systems. These companies are striving to innovate on desiccant chemistry, regeneration efficiency, and system integration so that desiccant-based climate control becomes more cost-competitive and easier to deploy at scale.
They are also building strategic partnerships: for example, equipment manufacturers team up with building automation companies and mechanical contractors to install, commission, and maintain these systems efficiently. Demonstration projects, case studies, and pilot installations in high-profile commercial buildings are helping to build confidence among developers and facility managers.
Why This Market Is Important
The liquid desiccant HVAC systems market holds strategic importance far beyond just energy savings. These systems tackle a critical challenge in modern buildings — humidity control — in a more sustainable way. By decoupling moisture management from temperature control, they enable better indoor air quality, reduce the risk of mold and humidity-related damage, and improve occupant comfort.
From a sustainability perspective, liquid desiccant HVAC systems offer a pathway to decarbonize building cooling loads by leveraging low-grade heat and reducing reliance on energy-intensive refrigeration cycles. In industries where moisture control is not just about comfort but also about product quality or safety, these systems provide a strong value proposition.
For architects, engineers, real estate developers, and facility managers, liquid desiccant systems represent a forward-looking investment: one that aligns with green building mandates, cost optimization goals, and future regulatory trends.
Browse Full Report – https://www.factmr.com/report/liquid-desiccant-hvac-systems-market