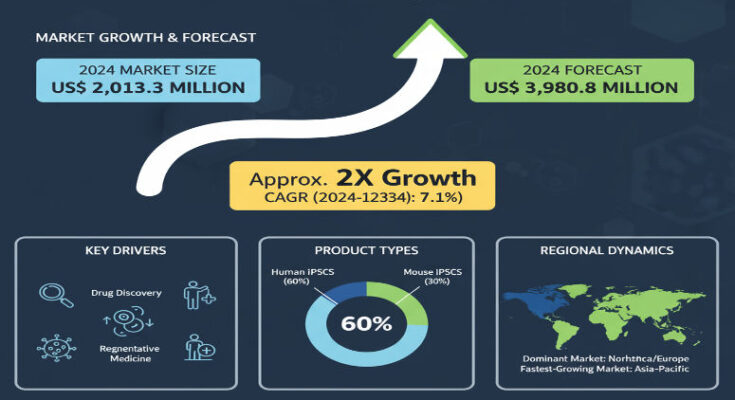
In 2024, the global Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Market is valued at roughly USD 2.01 billion. Projections estimate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 7.1% through 2034, rising to around USD 3.98 to 4.0 billion by that year. These figures reflect the expanding use of iPSCs in therapeutic pipelines, increasing R&D investments, improving automation in production, and broader adoption in preclinical and clinical research sectors.
Key Drivers Fueling the Market
Several interconnected forces are fueling this growth. First, rising chronic disease burden globally—neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases—increases demand for advanced regenerative solutions. Second, governments, research institutions, and private companies are investing heavily in developing iPSC-based therapies, disease models, and toxicity testing platforms. Third, technological advancements—especially in omics, genome engineering, and automation of iPSC derivation and maintenance—are improving yield, safety, and scalability. Fourth, there is growing regulatory and ethical clarity for iPSC applications, making commercialization more feasible. Finally, demand from precision medicine and personalized therapy markets is expanding, with iPSCs offering patient-specific modelling and treatment development.
Segments: Cell Types, Applications & End Users
Among different cell types, neurons are one of the fastest-growing segments, driven by neurological disease modelling, drug discovery targeting the brain, and research into disorders of the central nervous system. Other cell lineages (e.g. hepatocytes, fibroblasts, keratinocytes) also hold significant share, often depending on therapeutic area or application.
By application, regenerative medicine is expected to command a major portion of the market, with robust growth. Other significant applications include drug discovery, disease modelling, toxicity testing, and academic research. Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies lead among end users, accounting for a large share of current investment and product development. Academic and research institutions are also important players, especially for early-stage research and method development.
Regional Insights: North America & East Asia
North America currently leads the iPSC market. In 2024, it contributes almost half of the global market value. The region benefits from substantial funding for stem cell research, supportive regulatory environments, strong biotech and pharmaceutical industries, and infrastructure for clinical trials and commercialization. Over the forecast period, growth in North America remains healthy, though somewhat more moderate than in fast-emerging regions.
East Asia is emerging as one of the fastest growing markets. In 2024, it holds roughly 17–18% of the global market value, with projections of significantly higher growth rates through 2034. Countries in East Asia are investing aggressively in biotechnology, have lower cost structures for research and production, and are increasingly active in precision medicine and clinical translation, making them key future growth engines for the iPSC market.
Recent Developments & Innovation Highlights
Recent developments in the iPSC field highlight both progress and momentum. Several clinical trials leveraging iPSCs are underway, especially in regenerative medicine, to treat conditions like diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and ocular disorders. Companies are forming strategic partnerships and licensing deals for iPSC-derived therapies and cellular products. Innovation in automation and scalable manufacturing is underway to reduce cost and improve reproducibility. Omics-based tools (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics) are being used more heavily to characterize iPSCs and ensure safety, reducing risk of differentiation errors or tumorigenicity. Regulatory bodies are increasingly engaging in frameworks to evaluate iPSC therapies, which helps provide clearer pathways for commercialization.
Key Players & Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape includes established companies and well-funded startups. Key players include Thermo Fisher Scientific, FUJIFILM Cellular Dynamics, Fate Therapeutics, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Evotec SE, ViaCyte, Takara Bio, Axol Bioscience, REPROCELL USA, Cynata Therapeutics, and others. These companies are differentiating themselves through strength of cell lineages, purity, scalability, regulatory compliance, partnerships, and ability to deliver validated functional outcomes (e.g. successful differentiation, safety, integration in clinical pipelines). Some are also investing in automation, good manufacturing practice (GMP) capable facilities, and quality controls to reduce variability.
Challenges & Risks
Despite strong growth prospects, the iPSC market faces several challenges. High cost of GMP manufacturing and quality control remains a barrier, especially for smaller organizations. Differentiation protocols still suffer from variability; ensuring consistency, safety (especially avoiding tumorigenicity), and scalability is not trivial. Regulatory uncertainty in some jurisdictions can slow translation from lab to clinic. Intellectual property issues (patents, licensing) around reprogramming methods and cell line ownership are complex. Finally, market adoption depends not only on scientific advances but on reimbursement, clinical trial success, public acceptance, and ethical/regulatory oversight.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-ipsc-market
Outlook & Strategic Implications
Looking ahead to 2034, the iPSC market is expected to nearly double in value from its 2024 base. Key success factors for stakeholders will include investing in scalable and reproducible manufacturing, ensuring strong regulatory and safety credentials, focusing on high-growth applications (neurological, regenerative therapies, toxicity testing), and forging partnerships across research, clinical, and commercial sectors. Regions such as East Asia will likely outpace in growth rate, while North America and Europe will set standards and commercialize earlier. Companies that can lower cost of goods, increase cell line reliability, and demonstrate clinical efficacy will capture leadership in this evolving field.