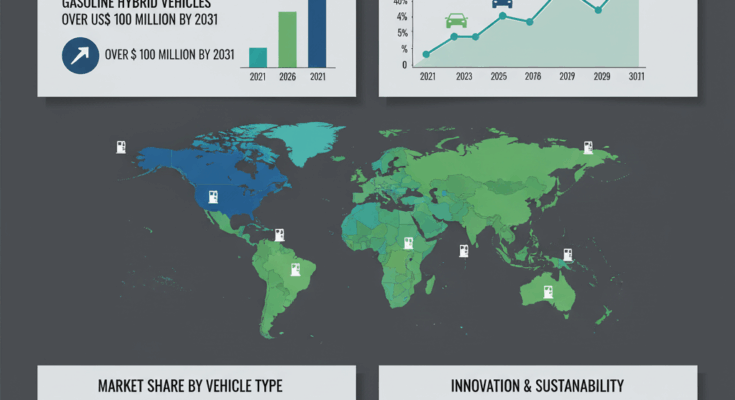
The global hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) market is on the cusp of a major upswing. The market size is projected to follow a stellar growth trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 14 % over the forecast period from 2021 to 2031. In monetary terms, gasoline hybrid vehicles alone are expected to surpass a valuation of over US$ 100 million by 2031. In 2021, the overall market was estimated around US$ 29 billion, driven by rising consumer preference for efficiency, environmental consciousness, and stricter emissions regulations.
Segmentation: Power Source, Powertrain & Vehicle Type
To understand the market comprehensively, it is crucial to examine hybrid electric vehicles through the lenses of power source, powertrain architecture, and vehicle type.
Power Source: Stored Electricity vs. On-Board Electric Generator
Stored Electricity HEVs rely on battery banks charged externally or through regenerative braking. These systems enable longer electric drive times and lower reliance on internal combustion engines under light load conditions. On-Board Electric Generator HEVs, on the other hand, generate electricity internally while driving. Although they require smaller batteries and offer flexibility, they provide limited pure electric range. Both categories are gaining momentum as automakers strive to optimize performance and cost efficiency.
Powertrain Architecture: Series, Parallel, and Combined Hybrids
Series hybrid vehicles operate by using the engine solely to power a generator that charges the battery, which then drives the electric motor connected to the wheels. Parallel hybrids allow both the engine and electric motor to drive the wheels directly, depending on driving conditions. Combined or power-split hybrids integrate both systems, switching dynamically between series and parallel modes for optimal performance. Power-split HEVs are becoming increasingly popular for their superior efficiency and balanced performance, and they are expected to dominate market revenues through 2031.
Vehicle Type: Passenger, Commercial, Two-Wheelers, and Others
The passenger vehicle category represents the largest segment of hybrid electric vehicles worldwide. Growing consumer awareness, rising fuel prices, and supportive government policies have driven adoption across major automotive markets. Commercial hybrid vehicles, including delivery vans, buses, and light trucks, are also gaining prominence due to their ability to reduce operating costs and meet sustainability targets.
Hybrid electric two-wheelers are particularly relevant in developing economies such as India and Southeast Asia, where they serve as affordable, efficient commuting options. Additionally, other niche vehicle types, including hybrid golf carts and specialized off-road vehicles, contribute to the broader market landscape.
Regional Landscape & Market Territories
The hybrid electric vehicles market is witnessing growth across multiple regions. Europe is projected to lead in terms of revenue share, accounting for nearly 16 % of the global market by 2031. Stringent emission standards, environmental awareness, and extensive infrastructure development are driving adoption in this region.
Asia-Pacific, including China, India, and Southeast Asia, is another key growth hub. India alone is expected to capture about 20 % of the global share by the end of the forecast period, supported by government initiatives like the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) program. North America is also expanding steadily, with the United States at the forefront due to supportive regulations, growing infrastructure investment, and increasing consumer acceptance of hybrid models.
Other regions such as Latin America, the Middle East, Africa, and Japan show varied adoption patterns influenced by infrastructure readiness, energy policies, and market maturity.
Recent Developments & Competitive Landscape
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming the hybrid electric vehicle landscape. Automakers have launched new models that combine efficiency and performance. Ford introduced the Mustang Mach-E, showcasing how hybrid and electric technologies can coexist in mainstream consumer vehicles. Innovations in power management software are enabling better energy distribution between electric and combustion systems, improving overall fuel efficiency by up to 50 %.
In battery technology, emerging concepts like refillable flow batteries promise ultra-fast recharging, potentially addressing range anxiety issues. Energy companies are also adapting to the electrified future. For example, lubricant manufacturers have developed specialized fluids to meet the unique cooling and performance requirements of hybrid drivetrains, ensuring longer component lifespans and optimal system efficiency.
The competitive landscape of the hybrid electric vehicles market is dynamic, with both traditional automakers and new entrants vying for dominance. Major companies such as Toyota, Honda, Ford, Nissan, and Daimler are leading the charge. Toyota continues to innovate in its hybrid portfolio, building on the success of the Prius. Honda’s intelligent multi-mode hybrid systems have improved power efficiency and reduced emissions. Ford and General Motors are leveraging hybrid technology as a stepping stone toward full electrification.
Component manufacturers, including ZF, BorgWarner, Continental, and Schaeffler, play a critical role in advancing hybrid powertrain efficiency and reliability. These firms focus on lightweight materials, enhanced motor design, and intelligent control systems to reduce costs and improve performance. Energy and infrastructure companies are also expanding their footprint through investments in charging networks and hybrid-specific solutions.