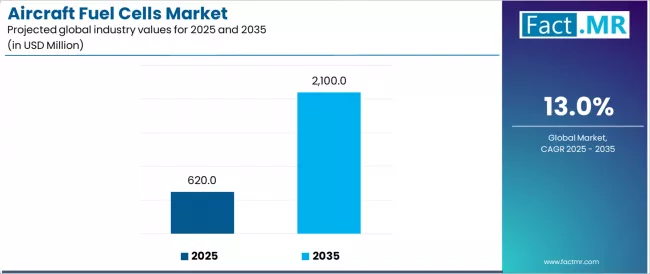
As the aviation industry faces increasing regulatory pressure to cut emissions and transition toward sustainable propulsion systems, fuel cell technology is emerging as a promising pathway for cleaner and more efficient aircraft operations. The aircraft fuel cells market is evolving rapidly as manufacturers, researchers, and aviation authorities explore hydrogen-based and hybrid-electric systems capable of reducing carbon footprints, lowering operating costs, and supporting long-term climate goals.
What Are Aircraft Fuel Cells?
Aircraft fuel cells are electrochemical devices designed to convert the energy stored in fuels—typically hydrogen—into electricity through controlled chemical reactions. Unlike conventional combustion engines, fuel cells generate power without burning fuel, resulting in minimal emissions. Water vapor and heat are the primary byproducts of hydrogen fuel cell systems, making them among the cleanest energy sources for aviation applications.
Fuel cells differ from batteries in that they are capable of continuously generating electricity as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. This makes them suitable for a range of onboard uses such as propulsion, auxiliary power, and emergency power support.
Why the Market Is Growing
One of the strongest drivers of market expansion is the global push toward decarbonizing the aviation sector. Airlines, aircraft manufacturers, and governments are actively seeking alternative propulsion methods that can significantly cut emissions. Fuel cells, especially hydrogen fuel cells, are gaining attention for their ability to offer high energy efficiency without contributing to atmospheric pollution.
Technological advancements are also accelerating adoption. Modern fuel cells—particularly Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)—are becoming lighter, more efficient, and more durable. Their improved power density makes them a suitable fit for aircraft, where weight and efficiency are crucial performance parameters.
Hybrid-electric systems, which combine fuel cells with lithium-ion batteries, are likely to dominate early adoption. Fuel cells can supply steady, long-duration power, while batteries can support peak loads during takeoff, landing, and rapid maneuvering. This combination provides a balanced and efficient power architecture for next-generation aircraft.
Noise reduction is another factor driving interest. Fuel cell systems operate far more quietly than combustion engines, making them ideal for urban air mobility (UAM), electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, and other emerging aviation platforms that aim to operate in noise-sensitive environments.
Government initiatives, funding programs, and regulatory frameworks in many countries are providing additional support. Grants, research collaborations, and hydrogen-investment roadmaps are helping fuel cell developers and aircraft makers accelerate innovation.
Key Market Challenges
Despite their promise, aircraft fuel cells must overcome several barriers before they achieve large-scale commercial adoption.
High Cost:
Fuel cell systems require advanced materials, precision engineering, and rigorous testing. This makes them more expensive compared to conventional propulsion options. Certification processes in aviation further add to development costs.
Hydrogen Infrastructure:
Hydrogen production, storage, and refueling infrastructure for aviation remains underdeveloped. Hydrogen’s low volumetric energy density necessitates specialized storage tanks and cryogenic or high-pressure systems, which introduces complexity and additional costs for airlines and airports.
Safety and Certification:
The aviation industry is extremely risk-sensitive. Any new power technology must undergo extensive certification to comply with safety, reliability, and performance standards. The process is rigorous and time-consuming, particularly for new propulsion technologies.
Market Segmentation: Types, Technologies & Applications
The aircraft fuel cells market can be viewed across multiple segments:
Fuel Type:
Hydrogen fuel cells dominate the landscape due to hydrogen’s high energy-to-weight ratio and zero-emission profile. Methanol and biofuel-based fuel cells exist but remain limited in aviation applications due to lower efficiency and higher emissions compared to hydrogen.
Technology:
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs): Lightweight, efficient, and suitable for aircraft.
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs): High efficiency but heavier and more heat-intensive.
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFCs): Less common due to complex operating conditions.
Application Areas:
Fuel cells can be used for:
- Auxiliary Power Units (APUs)
- Primary propulsion systems
- Backup and emergency power systems
- Hybrid-electric propulsion architectures
Aircraft Categories:
Applications span commercial aircraft, business jets, military platforms, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and new-age eVTOL and UAM platforms.
Regional Market Dynamics
The global aircraft fuel cells market is expanding across several regions:
- North America is advancing fuel cell research and hybrid-electric aircraft programs due to strong aerospace infrastructure and government-supported hydrogen initiatives.
- Europe remains a leading region due to its aggressive decarbonization policies, hydrogen strategies, and collaborations between aerospace companies and fuel cell developers.
- Asia-Pacific is emerging rapidly, with countries like China and Japan investing heavily in hydrogen technologies and clean aviation.
Each region is shaping the market differently, but all share a common vision: transitioning from fossil fuel dependency to low-emission aviation.
Key Players and Industry Collaborations
Several major aerospace companies, fuel cell manufacturers, and energy innovators are driving the market forward. Aircraft manufacturers are developing experimental hydrogen-powered planes and working closely with fuel cell companies to integrate these systems into future aircraft designs.
Partnerships are becoming increasingly common as companies collaborate on hydrogen storage systems, lightweight materials, and power management solutions. The integration of cryogenic storage, high-pressure fuel delivery systems, and advanced thermal management is essential for successful commercialization.
Future Outlook: Transition Toward Zero-Emission Flight
The aircraft fuel cells market is set to play a significant role in the next evolution of sustainable aviation. Major trends expected to shape the future include:
- Wider adoption of hybrid-electric propulsion systems
- Scaling of hydrogen infrastructure at airports
- Increased R&D investment in lightweight materials
- Integration of fuel cells into eVTOL and urban mobility aircraft
- Stronger government policies supporting zero-emission aviation
As the world moves toward carbon-neutral transportation, aircraft fuel cells offer a practical and innovative solution for reducing emissions, lowering noise levels, and enabling new energy-efficient aircraft designs.
Browse Full Report – https://www.factmr.com/connectus/sample?flag=S&rep_id=8794