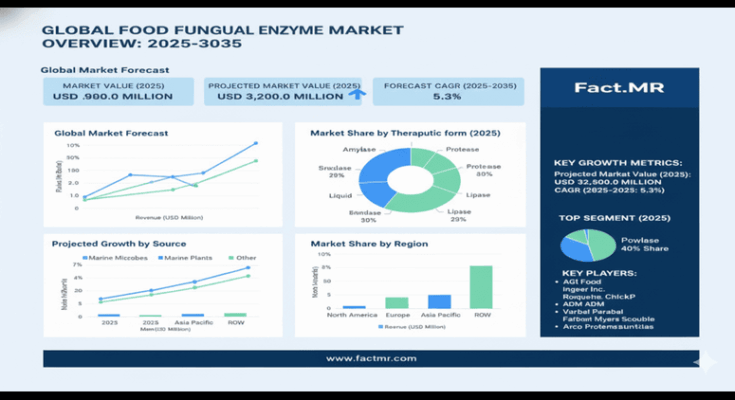
The global Food Fungal Enzyme Market is entering a decade of strong expansion, growing from USD 1,900.0 million in 2025 to USD 3,200.0 million by 2035 at a compound annual growth rate of 5.3%. This steady increase underscores a structural transition within the food processing industry, where fungal enzymes are becoming essential tools for improving product quality, production efficiency, and sustainability across bakery, beverage, and dairy applications.
Fungal enzymes have become a cornerstone of the clean-label revolution, helping food manufacturers achieve the texture, stability, and shelf-life improvements once possible only with synthetic additives. Their status as “processing aids” in most global regulations means they can deliver performance benefits without adding to ingredient declarations, giving manufacturers a critical advantage in maintaining simple, transparent product labels. This dual role of functionality and regulatory simplicity has fueled widespread adoption across industrial food segments worldwide.
The Food Fungal Enzyme Market continues to expand rapidly within bakery applications, which account for approximately 40% of total usage. Fungal amylases and proteases improve dough rheology, texture, and softness, supporting large-scale industrial baking systems where consistency and efficiency are paramount. In beverages, fungal enzymes such as pectinase and cellulase enhance juice extraction and clarity, helping producers achieve higher yields and superior flavor retention. The dairy sector, meanwhile, benefits from lipases and proteases that accelerate flavor development and texture refinement in cheese, yogurt, and milk processing. Collectively, these enzyme applications deliver efficiency gains of up to 60% compared with conventional chemical or mechanical processing methods.
Between 2025 and 2030, the Food Fungal Enzyme Market is expected to expand from USD 1,900.0 million to USD 2,500.0 million, driven by modernization initiatives, food technology investments, and policy support for sustainable processing. From 2030 to 2035, the market will continue to accelerate, adding another USD 700.0 million in value as automation and high-purity enzyme production technologies mature. Precision fermentation and multi-activity enzyme formulations are emerging as transformative innovations, enabling consistent global food production while reducing variability in processing outcomes.
Regionally, Asia Pacific remains the fastest-growing hub for the Food Fungal Enzyme Market. India and China lead global expansion, posting expected CAGRs above 5.8%, supported by government-backed food technology programs, domestic enzyme manufacturing infrastructure, and growing demand for processed and fortified foods. Developed markets, including the United States, Germany, Japan, and South Korea, continue to dominate in high-value enzyme innovation and standardization. These regions prioritize high-purity fungal enzyme production for premium applications in bakery and beverages, reinforcing the importance of advanced fermentation capabilities.
The competitive landscape of the Food Fungal Enzyme Market remains moderately consolidated, with approximately 15 to 20 major companies controlling nearly half of global revenues. Key industry leaders such as Novozymes, DSM, AB Enzymes, DuPont, BASF, Amano, Kerry, and Chr. Hansen maintain their positions through technological leadership, scale advantages, and long-term partnerships with global food producers. The competition has increasingly shifted from price-based differentiation to innovation-driven strategies focused on enzyme efficiency, purity, and customization for application-specific performance. In emerging markets, regional players are entering the field with cost-effective fermentation systems that cater to local processing requirements and government-backed food modernization efforts.
For manufacturers and ingredient suppliers, the Food Fungal Enzyme Market offers several strategic advantages. First, fungal enzymes support sustainability by reducing food waste, energy use, and reliance on synthetic processing aids. Second, they enable clean-label differentiation, allowing food brands to meet rising consumer expectations for natural and transparent ingredients. Third, fungal enzymes enhance profitability by improving yields, reducing batch times, and extending product shelf life. Fourth, they offer scalable opportunities in high-growth Asian markets where food processing is expanding rapidly. Finally, manufacturers benefit from collaborative R&D with enzyme technology firms that are constantly developing next-generation enzyme solutions for complex food systems.
As the Food Fungal Enzyme Market evolves, technology will play a decisive role. Advances in precision fermentation, microbial strain optimization, and enzyme stabilization will drive the next wave of efficiency and product innovation. Additionally, government incentives for sustainable food production are accelerating enzyme adoption, particularly in emerging economies seeking to strengthen domestic food industries.
By 2035, the Food Fungal Enzyme Market will have transitioned from a specialized niche to a fundamental component of modern food processing. Its importance will continue to grow as global food producers strive for higher quality, safety, and sustainability standards. The convergence of biotechnology and food manufacturing ensures that fungal enzymes will remain at the forefront of innovation for decades to come.
The Food Fungal Enzyme Market therefore represents a pivotal opportunity for both established ingredient manufacturers and emerging biotech firms. Companies investing today in production technology, regional infrastructure, and application-specific enzyme development are likely to capture significant long-term advantages in cost efficiency, product quality, and market credibility.
Browse Full Report : https://www.factmr.com/report/food-fungal-enzyme-market
In summary, the Food Fungal Enzyme Market is set to redefine the global food processing landscape by aligning technological advancement with consumer expectations for cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable foods. It stands at the intersection of science, efficiency, and natural innovation—an industry poised for continuous transformation and growth through 2035 and beyond.