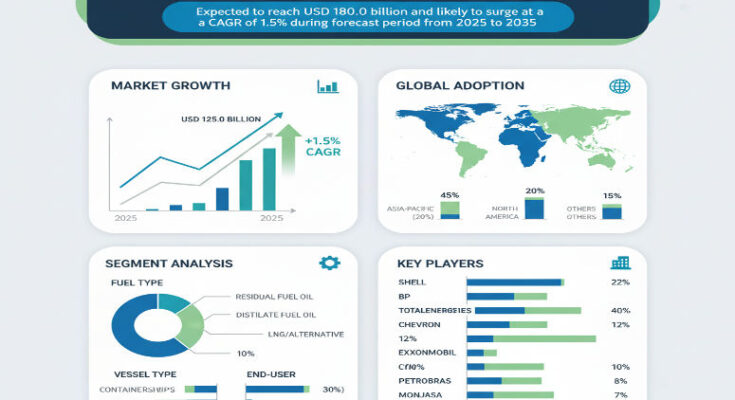
The global bunker fuel market is forecast to grow modestly from USD 155.0 billion in 2025 to about USD 180.0 billion by 2035, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 1.5% over the period. This growth reflects the evolving landscape of marine fuel supply, regulatory compliance, shipping demand, and fuel segmentation, as maritime operators seek more efficient and compliant fuel options while global trade continues to expand.
Market Drivers & Growth Catalysts
Several structural factors are driving the bunker fuel market. Global sea trade remains a key backbone for international commerce, with fleet expansions and shipping volumes increasing demand for marine fuels. Vessels continue to require reliable fuels to power long-distance voyages, container trade, bulk carriers, tankers, and other maritime logistics. The shift toward cleaner fuel types or low-sulphur blends is driven by regulatory mandates (e.g. limits on sulphur content), pushing shipping companies toward compliant fuel options. Operators are increasingly adopting fuels that meet stricter environmental requirements while balancing operational cost and supply logistics.
Also, ports and bunkering hubs are enhancing infrastructure and refining supply chains to support a variety of fuel types — from very low-sulphur fuel oil (VLSFO) to marine gas oil, high-sulphur fuel oils (with scrubbers), and even alternative or blended fuels. These developments help shipping companies manage compliance, fuel quality, and logistical coordination across vessel types and trade routes.
Product / Fuel Type & Application Segments
Within bunker fuels, different fuel grades or fuel types play distinct roles. VLSFO (very low-sulphur fuel oil) often dominates in many shipping operations because of its compliance with emission standards and its suitability for large commercial vessels. Other fuel types like marine gas oil or MGO, marine diesel oil, heavy fuel oils with scrubbers, or alternative fuels blended with biofuels or LNG are also part of the market mix.
By vessel type or application, container ships, bulk carriers, tankers, and other large commercial vessels consume a large share of bunker fuel. Container vessels often drive high demand on long-haul and high-frequency routes, while bulk carriers and tankers contribute based on cargo volumes and distances. Bunkering operations at key port hubs and refuelling infrastructure are important components of the supply chain, supporting fueling of vessels in transit and at port.
Regional Outlook & Growth Opportunities
Certain regions play a pivotal role in the bunker fuel market dynamics. Major bunkering hubs in regions like East Asia and Western Europe are essential for global shipping fuel supply due to their port infrastructure, storage, refining and bunkering capacities. These hubs serve vessels on long trade routes and support large volumes of fuel supply. Emerging regions such as the Middle East also play a critical role due to proximity to shipping lanes and oil supply.
The Asia-Pacific region is particularly important given high volumes of maritime trade, container shipping, and long sea routes. Many ports in Asia serve as bunkering hubs, supporting both inbound and outbound vessels. Meanwhile, mature markets in North America and Europe also maintain demand, especially where regulatory requirements for low-sulphur or alternative fuels are more stringent. These regions are upgrading bunkering infrastructure, refining fuel blends, and responding to environmental regulations. Other regions such as Latin America or Africa may see gradual growth as maritime trade expands and port infrastructure develops.
Competitive Landscape & Strategic Trends
The bunker fuel market includes major energy companies, refinery operators, bunker suppliers, bunkering hubs, and logistics / marine fuel providers. Key players compete on reliable supply, fuel quality, compliance with sulphur and emission standards, and ability to supply various fuel grades (low-sulphur, scrubber-compatible high-sulphur, alternative fuels). They also manage logistics, storage, blending, delivery coordination, and quality assurance to meet vessel requirements.
In recent years, suppliers have expanded bunkering infrastructure in major ports, increased storage capacity, and improved fuel blending and testing capabilities. Some providers offer integrated services including fuel delivery, quality testing, fuel traceability, and compliance verification, helping shipping companies ensure that fuel meets required specifications and emission regulations.
Challenges & Market Restraints
Despite continued demand, there are challenges. Regulatory compliance (regulations on sulphur content and greenhouse gas emissions) requires shipping companies to upgrade to cleaner fuels or invest in exhaust scrubbers, increasing costs and affecting fuel demand patterns. Economic fluctuations and slower global trade growth may dampen growth in future marine fuel demand. The rise of alternative or dual-fuel vessels using LNG or biofuels may gradually reduce dependence on conventional bunker fuel grades.
Fuel price volatility, logistics constraints, and variable fuel quality across ports also pose challenges for shipping operators. Bunker suppliers must maintain high quality, manage blending, and ensure consistent compliance across different fuel types. The cost of fuel upgrades or retrofitting vessels may also influence demand.
Forecast & Strategic Recommendations
With the market expected to grow from USD 155.0 billion in 2025 to USD 180.0 billion by 2035 at a 1.5% CAGR, the bunker fuel industry shows modest but steady growth over the decade. Stakeholders should invest in bunkering infrastructure upgrades, storage capacity expansion, and quality control in bunkering operations. Suppliers may also invest in alternative fuels and blends to address environmental regulation and provide compliant options (low-sulphur, bio-blends, LNG bunkers).
Ports can upgrade supply chains and bunkering logistics to meet demand from large vessel fleets. Shipping companies should evaluate fuel procurement strategies, compliance options (use of low-sulphur or scrubber solutions), and consider alternative fuel adoption where economically feasible.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/bunker-fuel-market
Editorial Perspective
Bunker fuel remains a cornerstone of maritime logistics and global trade. As shipping continues supporting supply chains and global commerce, fuel supply, compliance and infrastructure play vital roles. Even with modest growth, the bunker market will continue evolving through regulatory shifts, infrastructure enhancements, and adoption of cleaner fuel alternatives. Companies that adapt to changing regulations, invest in infrastructure, and supply compliant fuel options will be well-positioned to navigate this market through 2035.