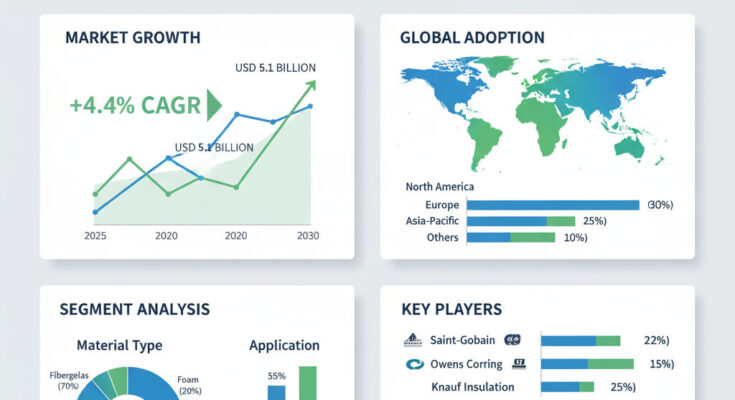
The glass insulation market is on an upward trajectory as building owners, developers and industrial operators increasingly prioritize energy efficiency, thermal comfort and regulatory compliance. Market analysts estimate that in 2025 the market value is about USD 5.4 billion, rising to USD 8.3 billion by 2035, which corresponds to a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% over the the decade. This steady growth reflects growing adoption of advanced glass insulation technologies across residential, commercial, and industrial segments, as well as tighter building codes, retrofitting demand, and rising awareness of the role of insulation in reducing energy costs and carbon footprints.
Key Drivers & Market Catalysts
Several interlinked factors are driving growth in glass insulation. In the construction sector, strict energy-efficiency standards increasingly require glazing systems or insulation materials that reduce heat transfer through windows, walls or facades. Glass insulation technologies—such as insulating glass units, cellular or wool glass insulation boards—play a key role in meeting those requirements. Retrofit activity in older buildings also adds momentum, as existing structures upgrade to double or triple glazing or improved insulating glass to reduce energy consumption and heating or cooling loads. On the industrial side, process, HVAC systems and storage facilities also demand insulation that can tolerate thermal cycles and maintain performance under various conditions. Sustainability and regulatory pressure are pushing developers and manufacturers to adopt materials that improve energy performance and reduce greenhouse-gas emissions, making glass insulation an attractive component of green construction projects.
Product & Application Segmentation
The market is segmented by product types and application categories. Key product types include insulating glass units (IGUs) that use multiple panes, inert gas fills, spacer technologies and coatings; cellular glass insulation boards that provide rigid, moisture-resistant insulation used in structural or industrial contexts; and glass wool or fiber glass wool, which offers flexible insulation used in walls, roofs, HVAC ducts, and other spaces requiring thermal or acoustic insulation. On the application side, residential construction (new homes or retrofits) remains a core demand driver, especially for windows, facade glass insulation and energy-efficient renovations. Non-residential and commercial construction is also significant, covering offices, retail, hotels, institutional buildings, and industrial facilities with HVAC or facade insulation needs. Industrial applications include insulation of pipes, storage tanks, refrigeration systems, and manufacturing processes.
Regional Insights & Growth Opportunities
Regionally, mature markets like North America and Europe continue to adopt glass insulation technologies due to established construction industries, stringent building codes, well-developed supply chains, and high awareness of energy efficiency. These regions often lead in retrofit activity, adoption of advanced insulating glass units (double or triple glazed units), and compliance with energy performance standards. In contrast, the Asia-Pacific region emerges as one of the fastest-growing markets. Rapid urbanization, rising incomes, expanding construction of residential and commercial buildings, and upgrading of building envelopes are driving demand. Many countries in Asia are enforcing building energy codes and investing in modernization of older building stock, accelerating uptake of insulating glass, glass wool insulation, or rigid boards. Emerging markets in Latin America, Middle East & Africa also show potential though growth is somewhat slower due to cost constraints or limited retrofit cycles currently.
Competitive Landscape & Industry Trends
The competitive landscape is populated by established manufacturers of glass insulation products (glass wool, cellular glass boards, insulating glass units) as well as insulation system integrators. Key players in the the market include large manufacturers of glass and insulation materials, companies that produce multi-pane insulating glass units, and suppliers of rigid or flexible glass insulation products. These companies continuously invest in improving material formulations—e.g. lower thermal conductivity, better moisture resistance for cellular glass, lower expansion in IGUs, better acoustic performance, and lighter materials.
Industry trends include increased use of double glazing and transition toward triple glazing in new and retrofit buildings as energy performance requirements tighten. Another trend is integration of insulating glass units with building automation or smart glazing (coated or low-emissivity glass plus inert gas fills) that improves thermal insulation without sacrificing natural light. On the the industrial side, demand for rigid cellular glass or board insulation for pipes, tanks, and HVAC ducts is rising because of improved material characteristics (moisture resistance, compressive strength, durability under temperature cycling).
Challenges & Market Restraints
Despite the favorable outlook, there are some constraints. The upfront cost of high-performance glass insulation (multi-pane glass, specialized coatings or rigid cellular boards) can be higher than conventional insulation materials or single glazing, which may slow adoption in cost-sensitive projects or in emerging markets. Installation of insulating glass units requires proper framing, seal integrity and quality control to avoid leakage or thermal performance degradation over time. Rigid or cellular glass boards may require specialized cutting or installation techniques, increasing labor costs or installation complexity. In addition, variances in building code enforcement or local standards can slow adoption in regions where insulation regulations are weaker or not strictly enforced.
Forecast & Strategic Recommendations
Looking ahead to 2035, the glass insulation market is expected to grow steadily from USD 5.4 billion in 2025 to USD 8.3 billion, with a CAGR of 4.4%. Companies in this sector should focus on continuing R&D to reduce thermal conductivity, improve strength and durability of insulating glass units or rigid boards, and develop cost-effective solutions that suit diverse climate conditions. Expanding manufacturing or distribution in high growth regions such as Asia-Pacific can capture rising retrofit and new construction demand. Offering bundled solutions—insulating glass units + installation + performance testing or certifications—can help reduce barriers for developers or homeowners. Partnerships with construction contractors, HVAC firms or architectural glass fabricators can help drive adoption.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/glass-insulation-market
Editorial Perspective
Glass insulation is becoming a key enabler in the shift toward sustainable, energy-efficient built environments. As buildings evolve, glazing systems and insulating materials are no longer afterthoughts but critical components of envelope design. Whether residential homes upgrading windows or commercial buildings pursuing green ratings, insulation in glass form or rigid boards plays a central role. Over the next decade, as standards tighten and developer awareness increases, glass insulation will increasingly be specified for both thermal and acoustic value. Companies that innovate in material performance and regional deployment will be well positioned to benefit from the projected growth and become integral partners in global construction modernization.