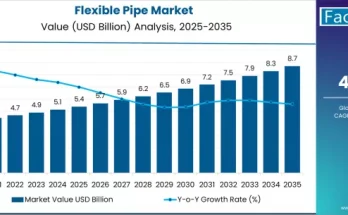
With the ever-increasing penetration of electronic devices across the globe, the problem of electronic waste has grown more complex and urgent. In response, the electronics recycling market is gaining prominence as an essential pillar of the circular economy. This market plays a pivotal role in minimizing environmental impact, conserving finite resources, and supporting sustainable technological growth. As industries, governments, and consumers become more environmentally conscious, recycling electronic waste is transitioning from a regulatory requirement to a strategic imperative.
Market Overview:
The electronics recycling market comprises processes and services that recover valuable materials from discarded electronic devices, ranging from smartphones and laptops to large industrial equipment. These processes include collection, dismantling, material separation, and recovery of precious and base metals, plastics, and glass. The growing lifespan of devices, consumer awareness, stricter environmental regulations, and advancements in recycling technologies are collectively driving the demand for efficient and scalable electronics recycling solutions.
Additionally, the market is witnessing increased investment from tech giants and governmental bodies alike, underscoring a systemic shift toward sustainable electronics lifecycle management. From environmental compliance to resource optimization, electronics recycling is no longer a secondary consideration—it’s a foundational element of responsible electronics production and consumption.
Regional Insights:
North America:
North America remains a leader in electronics recycling adoption due to established infrastructure, stringent e-waste regulations, and corporate ESG commitments. The presence of advanced recycling facilities and a growing emphasis on producer responsibility laws supports strong regional growth. Moreover, North American tech companies are increasingly prioritizing circular design principles, further reinforcing recycling initiatives.
Europe:
Europe continues to be at the forefront of electronics recycling due to robust regulatory frameworks like the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive. EU nations are promoting take-back schemes and green public procurement practices, encouraging both businesses and consumers to participate in electronics recycling. Cross-border collaborations and investments in innovation further bolster Europe’s status as a mature and dynamic market.
Asia-Pacific:
Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly evolving market, propelled by rising consumer electronics usage and increasing government awareness of e-waste hazards. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are investing in formalizing recycling sectors, supporting local recyclers, and launching educational initiatives. Though informal recycling is still prevalent in some areas, there is a clear transition toward structured, regulated recycling ecosystems.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa:
These regions are gaining attention for their untapped recycling potential. While challenges such as limited infrastructure and public awareness exist, policy developments and international partnerships are setting the stage for future growth. Efforts to build local e-waste management networks are underway, with an eye on economic development and environmental protection.
Key Trends & Forecast:
- Circular Economy Integration:
Recycling is no longer viewed as an end-of-life activity but as an integral component of the product lifecycle. Electronics manufacturers are increasingly adopting design-for-recycling strategies to facilitate easy disassembly and recovery of materials. Partnerships between OEMs and recycling firms are expanding to ensure closed-loop systems.
- Regulatory Support and Compliance:
Global and regional policies are enforcing the extended producer responsibility (EPR) framework, which mandates electronics manufacturers to manage the post-consumer phase of their products. Compliance with such regulations is shaping the strategies of both established companies and new entrants in the market.
- Advancements in Recycling Technologies:
The industry is witnessing rapid technological innovation in the form of AI-based material sorting, robotic disassembly, and chemical recycling methods. These solutions not only improve recycling efficiency but also reduce contamination, ensuring higher purity and value of recovered materials.
- Urban Mining and Metal Recovery:
As the demand for rare earth and precious metals grows, the concept of urban mining is gaining traction. Electronic waste is now being recognized as a rich resource for materials like gold, palladium, copper, and lithium. Efficient recovery of these metals is becoming a key driver for the market.
- Shift Toward Formalization:
In emerging economies, informal recycling practices often pose health and environmental hazards. However, there is a growing shift toward the formalization of the recycling sector through certification programs, training initiatives, and public-private partnerships that improve standards and sustainability.
- Consumer Participation and Awareness:
Rising awareness among consumers about environmental issues and the value of recycling is leading to improved e-waste collection rates. Incentive-based return programs and user-friendly collection systems are making it easier for individuals and small businesses to responsibly dispose of their outdated electronics.
- Expansion of Take-Back Programs:
Major electronics brands are launching take-back and buyback programs to recover used devices directly from consumers. These programs not only aid in recycling but also provide brands with materials for remanufacturing and refurbishing, contributing to cost efficiency and brand loyalty.
Applications & End-Use Outlook:
The demand for electronics recycling services spans across a wide range of industries:
Consumer Electronics:
Smartphones, tablets, televisions, and personal computers are the most commonly recycled devices. With rapid product obsolescence and high ownership rates, this category forms the backbone of the global recycling stream.
IT & Telecommunication Equipment:
Data centers, enterprise IT infrastructure, and telecom devices are being retired at a growing rate due to digital transformation. Enterprises are turning to certified recyclers to ensure secure and environmentally sound disposal of these assets.
Household Appliances:
Refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves are now subject to regulated recycling protocols in many regions. Their size and content make them a priority for responsible end-of-life treatment.
Industrial Electronics:
Sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and energy are generating a significant amount of e-waste through outdated machinery, monitoring systems, and control panels. Specialized recyclers are targeting these verticals with customized services.
Automotive Electronics:
With the rise of electric vehicles and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), there is a growing stream of electronic waste in the automotive sector. Recycling these components is crucial for managing both environmental impact and material scarcity.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its growth, the electronics recycling market faces several hurdles:
- Complex product design that hampers disassembly and material separation.
- Inconsistent regulations across regions, complicating global operations.
- Data security concerns related to improper disposal of IT hardware.
- Low collection rates in certain areas due to lack of awareness and infrastructure.
However, these challenges also open up substantial opportunities:
- Companies investing in eco-design and product modularity will find it easier to comply with recycling norms.
- Emerging markets offer untapped potential for collection, sorting, and processing infrastructure.
- Integration of blockchain for traceability in recycling chains is being explored for transparency and compliance.
- Establishing certified e-waste management hubs could boost employment and local economies.
Conclusion:
The electronics recycling market is no longer a niche sector—it is an indispensable part of the global effort to create a sustainable, resource-efficient future. As industries grapple with resource scarcity, environmental regulations, and stakeholder expectations, effective recycling systems offer both ecological and economic returns.
By aligning product design, supply chain management, and consumer behavior with circular economy principles, stakeholders can turn electronic waste from a liability into an opportunity. For policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike, the message is clear: recycling electronics is not just good practice—it’s a critical strategy for the digital age.
Organizations looking to make informed decisions and lead in sustainability should prioritize comprehensive market intelligence and proactive engagement in the evolving electronics recycling ecosystem.