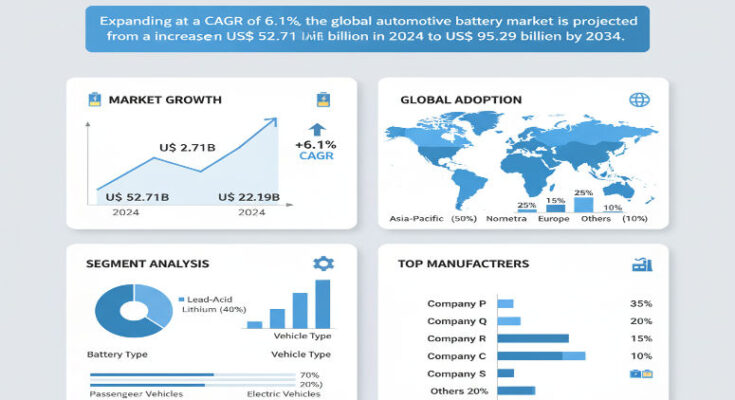
The global automotive battery market is undergoing a vital transformation, evolving from a component of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles into the backbone of electric mobility. In 2024, its value is estimated at US$ 52.71 billion, and it is projected to grow at a steady CAGR of approximately 6.1%, reaching around US$ 95.29 billion by 2034. This expansion reflects accelerating adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, improvements in battery technology, growing regulatory pressure for clean transport, and rising demand for performance and reliability from consumers worldwide.
What’s Driving Growth
Several major trends are fueling this robust expansion. First and foremost is the global push toward electrification: governments are implementing increasingly strict emission standards, subsidies and incentives for EV buyers, and mandates to phase out fossil fuel–powered vehicles. This creates strong demand for lithium-ion batteries and other high energy-density chemistries.
Second, advancements in battery technology are lowering cost per kWh, improving energy density, reducing weight, and enhancing safety. Breakthroughs in materials, cell design, fast-charging capability, thermal management, and battery management systems (BMS) are accelerating performance gains.
Third, rising consumer expectations are also shaping demand. Buyers of electric and hybrid vehicles expect longer range, quicker charging, and durable batteries that can support complex vehicle electronics, infotainment systems, and driver assistance features. Combined with expanding charging infrastructure, this reduces barriers to EV ownership.
Fourth, environmental awareness and sustainability considerations are contributing—automakers are investing not only in battery production but also in battery recycling and second-life applications, all part of broader sustainability strategies.
Segmentation Insights & Battery Types
The market comprises various battery types, notably lead-acid, lithium-ion, and to some extent nickel-metal hydride (for older or hybrid applications). Among these, lithium-ion is seeing the fastest growth and commanding increasingly large market value, particularly for electric propulsion, hybrid systems, and performance vehicles. However, lead-acid batteries remain important, especially for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) tasks in ICE vehicles and for aftermarket replacements, due to their lower cost and mature manufacturing base.
Vehicle type segmentation shows that passenger cars dominate current demand in terms of volume and value. Commercial vehicles, however, are growing faster in many forecasts, especially as logistics, public transit, and last-mile delivery shift toward electric or hybrid platforms.
Regional Outlook: United States, Asia-Pacific & Key Markets
North America is expected to hold substantial market share by 2034 (estimated at about 31.2%), driven by strong automaker investment, supportive policies, generous incentives, and rising consumer adoption of EVs. In particular, the United States is forecast to grow from about US$ 14.9 billion in 2024 to about US$ 23.75 billion by 2034. It remains a growth engine, especially for advanced battery technologies, automaker battery plants, and EV incentives.
Asia-Pacific is another key region and remains among the fastest growing, powered by China, South Korea, India, and Japan. China, in particular, has abundant capacity, raw material resources, strong government support, and a local supply chain that is increasingly mature. East Asia is projected to reach a battery market value of about US$ 26.78 billion by 2034. Local battery manufacturers there benefit from scale, vertical integration, and rapid domestic EV adoption.
Europe is making strides too, with regulatory pressure, domestic battery manufacturing investments, and increasing consumer demand for electrified vehicles. However, cost pressures, regulatory variation by country, and infrastructure rollout remain challenges.
Key Players & Insights
The competitive landscape includes global multinationals and regional specialists. Some of the prominent companies are:
-
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd. (CATL)
-
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
-
LG Energy Solution / LG Chem
-
Panasonic Corporation
-
BYD Company Ltd.
-
Hitachi Ltd.
-
GS Yuasa International Ltd.
-
Exide Industries Ltd.
-
Robert Bosch GmbH
-
A123 Systems LLC
These players are differentiating themselves through investment in research and development, expansion of manufacturing capacity, reductions in battery cost, improving energy densities, enhancing charging speed, integrating battery recycling and second-life use, and strategic partnerships (OEMs, governments, raw material suppliers).
For example, many are launching battery factories / gigafactories to localize production, reduce transportation costs, and secure supply chains. Some are also exploring new chemistries or battery formats (e.g. solid-state, battery modules with novel materials) to enhance safety, longevity, and performance.
Recent Developments & Innovation Signals
Recent industry activity highlights several noteworthy developments. Battery pack and cell makers are pushing down cost per kWh, making EVs more affordable. Fast charging capabilities are increasing; manufacturers are investing heavily in thermal management and connector designs to safely handle high-power charge currents. Battery recycling initiatives are gaining regulatory and commercial traction, with efforts to capture materials from spent cells and reuse or repurpose battery components.
There’s also growing interest in lightweight battery pack architectures and modular designs to improve vehicle efficiency. Innovations in battery management systems to prolong battery life and improve safety, especially in cold climates or under stressful operating conditions, are becoming standard.
Challenges & Restraints
Despite strong tailwinds, some challenges remain. The high cost of batteries—particularly raw materials like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and rare metals—is a key constraint. Supply chain disruptions (mining, refining, cell manufacturing) can inflate cost and delay production. Infrastructure for charging (public fast chargers, standardized connectors, grid capacity) remains insufficient in many regions. Safety concerns around thermal runaway, battery degradation, and recycling / disposal practices still require cautious design and regulation. Regulatory uncertainties, especially around content mandates, subsidies, import/export rules, and battery waste, can affect manufacturer planning and investment risk.
Another challenge is balancing performance vs cost: sometimes more durable, higher-energy batteries cost more, and cost sensitivity among consumers—particularly in emerging markets—can slow acceptance.
Browse Full Report: https://www.factmr.com/report/automotive-battery-market
Forecast & Strategic Takeaways
Over the 2024-2034 period, the automotive battery market is expected to nearly double in value globally. The biggest value will likely come from lithium-ion batteries for electric propulsion and hybrid systems. Lead-acid will remain relevant for legacy ICE vehicles and aftermarket replacements but will constitute a shrinking share over time.
Manufacturers with competitive advantage will be those who can reduce cost per kWh, ensure supply chain reliability, offer high energy density, fast charging, and durability, and integrate sustainability (recycling, second life) into battery lifecycle strategies. Collaborations and joint ventures, localizing manufacturing, investing in raw material sourcing and recycling, and aligning with policy incentives will be important.
For OEMs and governments, aligning incentives, subsidies, regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure (charging, recycling, grid support) will greatly influence how quickly battery adoption accelerates. Consumer education, performance guarantees, and lowering total cost of ownership (through long battery warranties, service networks, etc.) will help build trust and accelerate uptake, especially in new or emerging markets.