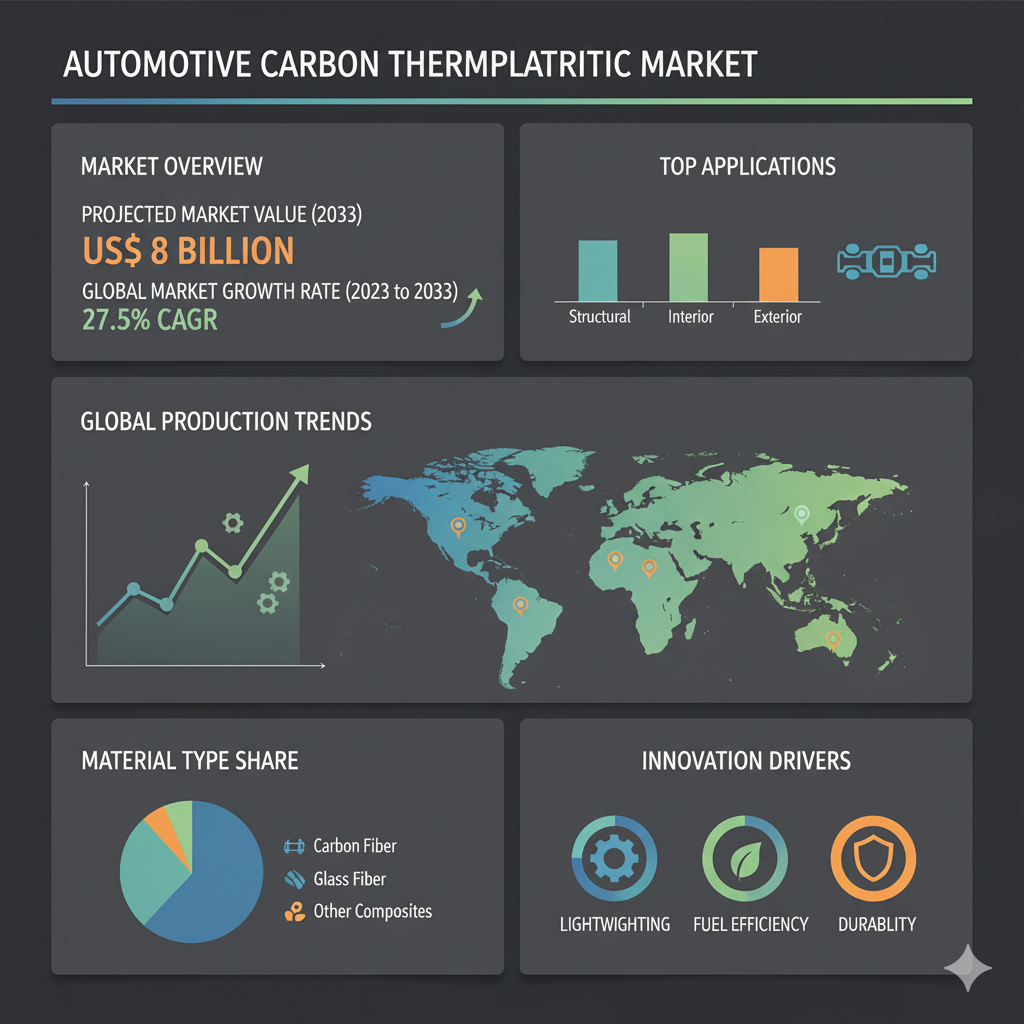
The global automotive carbon thermoplastic market is valued at US$ 700 million in 2023 and is expected to reach US$ 8 billion by 2033, rising at a high-value CAGR of 27.5% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033. This exponential growth reflects the industry’s commitment to innovation and sustainable design, aiming to deliver vehicles that are both efficient and high-performing.
Understanding the Market Dynamics
Automotive carbon thermoplastics are increasingly being adopted across various vehicle components due to their excellent mechanical properties, lightweight nature, and processing efficiency. These materials are helping automakers reduce vehicle weight by up to 50% compared to traditional metals, thereby improving fuel efficiency and reducing CO₂ emissions. The market is witnessing a transition from conventional thermoset composites to thermoplastic-based solutions, which offer advantages such as shorter production cycles, recyclability, and ease of repair.
As electric vehicle (EV) adoption accelerates, the demand for lightweight materials that can offset battery weight is expected to further fuel market growth. In addition, innovations in resin formulations and manufacturing technologies are enabling the mass production of carbon thermoplastic components, making them more accessible to mainstream automotive manufacturers.
Automotive Carbon Thermoplastic Market Analysis by Resin Type
The market can be analyzed based on key resin categories such as Polyamide (PA), Polypropylene (PP), Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), Polyetherimide (PEI), and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK). Each resin type offers distinct properties that influence its suitability for specific automotive applications.
Polyamide (PA) currently dominates market demand due to its excellent balance of strength, toughness, and impact resistance, which makes it ideal for structural and interior applications. Polypropylene (PP) is gaining popularity for its low density, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for exterior and semi-structural components. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), known for its superior thermal and chemical stability, is often used in under-hood parts exposed to high temperatures. Polyetherimide (PEI) offers exceptional flame resistance and UV stability, making it ideal for components that require long-term durability and aesthetic performance. Meanwhile, Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), though more expensive, provides outstanding mechanical strength and temperature resistance, finding use in high-performance and specialty automotive parts.
This resin-level diversification allows manufacturers to tailor material selection to meet specific performance, cost, and sustainability requirements, ensuring that carbon thermoplastics remain adaptable to diverse automotive applications.
Recent Developments and Industry Innovations
Recent years have seen a wave of technological advancements and strategic collaborations shaping the automotive carbon thermoplastic landscape. Leading material suppliers and automotive OEMs are investing heavily in research and development to enhance material performance and scalability. Innovations in continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastics have made it possible to produce complex, lightweight structures with high stiffness and impact resistance. Several companies are introducing next-generation carbon fiber composites that can be processed faster and integrated directly into vehicle production lines.
Collaborations between material producers and automotive manufacturers are also accelerating innovation. Partnerships focused on sustainable composite solutions, recycling technologies, and high-volume thermoplastic production are driving the industry toward circularity and cost reduction. Furthermore, startups and research institutions are exploring nanoparticle and additive technologies to enhance the performance of thermoplastic composites while reducing their overall manufacturing costs
Competitive Landscape and Market Strategies
The competitive landscape of the automotive carbon thermoplastic market is highly dynamic, with a mix of established global corporations and emerging innovators. Major chemical and material companies are focusing on vertical integration, combining resin production with composite manufacturing capabilities to strengthen their market position. These players compete primarily through product innovation, cost optimization, and long-term supply agreements with automotive OEMs.
Smaller players and startups, on the other hand, are carving out niches by developing proprietary material formulations and additive solutions that enhance composite performance. Many of them are targeting sustainability by introducing bio-based thermoplastics and recyclable composite systems. The overall competition is pushing the industry toward faster adoption, lower costs, and higher performance standards.
Regional Insights and Application Growth
Europe currently holds a dominant share of the global automotive carbon thermoplastic market, driven by stringent emission norms and a strong focus on electric mobility. Germany, with its well-established automotive manufacturing base, remains a key growth hub. North America follows closely, supported by increasing investment in lightweight composite research and a growing shift toward fuel-efficient vehicles. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region, led by Japan, China, and South Korea, is experiencing rapid adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, boosting demand for carbon thermoplastic materials.
Across the globe, these materials are increasingly used in vehicle exteriors, interiors, chassis structures, and under-the-hood components. As automakers seek to balance strength, aesthetics, and sustainability, carbon thermoplastics are becoming an integral part of modern vehicle design.