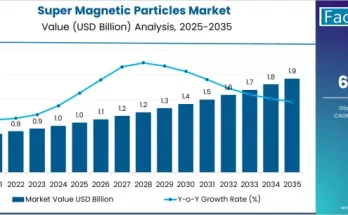
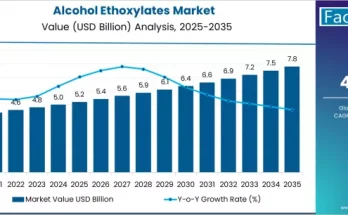
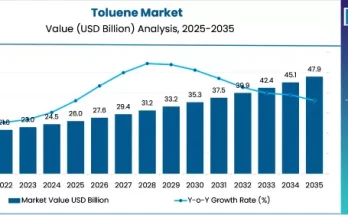
In today’s era of heightened environmental consciousness, the quest for sustainable solutions is more pressing than ever before. Amidst growing concerns about plastic waste and its detrimental impact on our planet, chemical recycling is gaining traction. While traditional recycling methods have made a significant impact, they often fall short in addressing the complexities of mixed and contaminated plastic waste. This is where chemical recycling steps in, offering a transformative approach that holds immense potential to reshape the future of plastic waste management.
Unraveling the Science of Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling, also known as advanced recycling or molecular recycling, is a process that aims to break down plastic waste into its constituent molecules or monomers. This is a departure from mechanical recycling, which involves melting down plastics to create new products but is limited by the quality and type of plastics that can be processed. Chemical recycling offers the advantage of dealing with a broader range of plastic types, including those that are typically challenging to recycle through conventional means.
The process of chemical recycling involves several innovative techniques, including pyrolysis, depolymerization, and solvolysis. Pyrolysis, for example, subjects plastics to high temperatures in the absence of oxygen, breaking them down into useful products such as fuels or feedstocks for new plastics. Depolymerization involves breaking the polymer chains into their individual monomer units, which can then be used to create new plastics with the same quality as virgin materials.
· Industry Partnerships and Investments:
Major players in the petrochemical and plastics industry are forming partnerships with startups and research institutions to invest in and develop chemical recycling technologies. This collaboration is accelerating the development and commercialization of these technologies, indicating the industry’s growing recognition of their potential. For instance,
o Shell, the energy and petrochemical company has partnered with several startups, such as Plastic Energy and Nexus Fuels, to develop and commercialize advanced recycling technologies. They aim to convert plastic waste into useful feedstocks and chemicals.
o Total Energies, a global energy company has invested in multiple chemical recycling projects, including partnerships with companies like Plastic Energy and Recycling Technologies, to support the development of advanced recycling processes.

· Government Support and Legislation:
Governments worldwide are recognizing the importance of chemical recycling in tackling plastic waste issues. They are introducing incentives, subsidies, and policy frameworks to encourage the adoption of chemical recycling technologies and to create a favorable regulatory environment for their growth. For instance,
o The EU has introduced regulations like the Single-Use Plastics Directive and the Circular Economy Action Plan, which encourage the use of chemical recycling to achieve plastic waste reduction targets.
o In the US, various states have introduced legislation to support chemical recycling. For example, the state of Illinois passed the Plastic Pyrolysis and Recycling Promotion Act to incentivize chemical recycling projects.
· Material Diversity:
Chemical recycling is gaining attention for its ability to handle a diverse range of plastic materials. Unlike traditional mechanical recycling, which can be limited by the types of plastics that can be processed together, chemical recycling can deal with mixed and complex plastic waste, including multilayer packaging and contaminated materials.
o For instance, Agilyx is a company that specializes in converting mixed plastic waste into high-quality feedstocks for new plastics production using pyrolysis technology. They can process a wide range of plastics, including polystyrene, polyethylene, and polypropylene.
· Circular Economy Alignment:
The concept of the circular economy, which promotes reducing, reusing, and recycling materials, aligns well with chemical recycling. This technology plays a crucial role in keeping plastics in circulation, reducing the need for virgin feedstocks, and closing the loop in plastic production.
o For instance, Veolia is a global waste management company that is actively involved in chemical recycling initiatives. They focus on transforming plastic waste into secondary raw materials that can be used for new plastic production.
· Reducing Carbon Footprint:

Chemical recycling has the potential to reduce the carbon footprint of plastics production. By using recycled plastic feedstocks, industries can significantly decrease the emissions associated with producing new plastics, contributing to sustainability goals.
o Carbios, a French company has developed an enzymatic recycling technology that breaks down PET plastics into their monomer building blocks. This process has the potential to significantly reduce the carbon footprint of PET production.
· Consumer Demand for Sustainable Products:
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, there is increasing demand for products made from recycled materials. Brands are responding by incorporating recycled plastics into their products, which in turn creates a more significant market for chemical recycling output. For instance,
o P&G: Procter & Gamble, through brands like Tide, has introduced detergent bottles made from recycled plastic, aligning with eco-friendly consumer preferences.
o Nestlé: Nestlé Waters uses recycled PET plastic in their water bottles, demonstrating their response to the demand for environmentally-conscious packaging.
· Plastic Waste Diversion from Landfills and Incineration:
Chemical recycling addresses the issue of plastic waste that would typically end up in landfills or be incinerated. This diversion of waste contributes to better waste management practices and a reduced environmental impact.
· Technological Scaling and Commercialization:
Over recent years, there has been progress in scaling up chemical recycling technologies from laboratory settings to commercial facilities. This trend showcases the industry’s commitment to making these processes economically viable and accessible. Some examples of the companies pursuing these activities:
o Loop Industries is known for scaling PET plastic depolymerization for new plastic production.
o Agilyx is a company that specializes in advanced recycling solutions for plastics. They have developed a pyrolysis technology that can convert mixed plastic waste into high-quality crude oil. The company has been working on commercializing its technology to tackle plastic waste issues.
· Rise of Startups and Innovation Hubs:
The chemical recycling landscape has witnessed the emergence of numerous startups and innovation hubs dedicated to developing novel technologies. This trend indicates a growing entrepreneurial interest in solving plastic waste challenges through technological innovation.
These trends collectively indicate a growing momentum in the adoption of chemical recycling as a critical tool in addressing plastic waste, fostering sustainability, and reshaping the future of plastics production and consumption.
Conclusion
The growing momentum in the adoption of chemical recycling signifies a significant shift towards a more sustainable and circular economy. With its ability to convert plastic waste into valuable raw materials, chemical recycling offers a promising solution to the global plastic pollution crisis. As governments, industries, and consumers increasingly recognize the urgency of addressing this issue, the demand for innovative and environmentally-friendly waste management strategies continues to rise.
The advancements in chemical recycling technology, coupled with the increasing investment and support from various stakeholders, provide a glimmer of hope for a future where plastic waste can be effectively transformed into valuable resources. However, it is crucial to ensure that the implementation of chemical recycling is accompanied by robust regulations, proper waste management practices, and continued research and development to maximize its potential and minimize any potential environmental risks. By embracing chemical recycling and transitioning towards a more circular approach, we can pave the way for a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable future for generations to come.